Single Articles
Best Practices
🔴 There Are 2 Ways to Violate 'S' in SOLID
This article delves into the complexities of the Single Responsibility Principle (SRP) in the context of iOS development. Using a case study of a TransactionCellView in a table view, it demonstrates how the addition of a button that alters the cell's layout based on specific conditions can lead to the violation of SRP. The article highlights the importance of avoiding the creation of "God objects" and over-abstraction, advocating for a refactor that moves decision-making logic out of the cell and into a more appropriate architectural layer. This ensures that each component retains a single responsibility, making the codebase more maintainable and scalable.
Details
URL: 🔗 There Are 2 Ways to Violate 'S' in SOLID
Published: April 30, 2021
Authors: Isaac Weisberg
Tags:
SOLID principles, Single Responsibility Principle, iOS development, Swift, software architecture
Key Points
- The article highlights two distinct ways in which the Single Responsibility Principle (SRP) can be violated in iOS development.
- The case study involves a
TransactionCellViewwhere the addition of a button based on conditional logic introduces multiple responsibilities within the cell. - The solution proposed involves refactoring to move decision-making logic out of the cell to ensure SRP compliance and maintain a clean architecture.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: Overview of the importance of SOLID principles in interviews and development.
- Case Study: Analysis of the
TransactionCellViewand how it violates SRP. - Problem Analysis: Discussion on the problems of having a single class handling multiple responsibilities.
- Solution: Detailed refactor proposal to restore SRP by moving logic out of the cell and into a dedicated layer.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 SOLID Principles Explained: A comprehensive guide to SOLID principles in software development.
- 🔗 Refactoring Techniques: Tips and techniques for effective code refactoring.
- 🔗 iOS Architecture Patterns: An overview of different architecture patterns used in iOS development.
🔵 Writing Good Unit Tests
This article by Chris Mash, published on Dev Genius, delves into the principles of writing effective unit tests in software development. It highlights the importance of having "good" unit tests that validate code behavior accurately, ensuring the reliability of your codebase during refactoring or updates. The article also explores Test Driven Development (TDD) as a method to foster better unit testing practices.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://blog.devgenius.io/writing-good-unit-tests-2158be9ee82d
Published: October 17, 2023
Authors: Chris Mash
Tags:
unit-testing, software-development, TDD, iOS
Key Points
- Importance of Good Unit Tests: Good unit tests ensure that the code behaves as expected by isolating the subject under test and providing meaningful coverage.
- Examples of Poor vs. Improved Tests: The article offers concrete examples of how to improve test cases, making them more likely to catch issues.
- Test Driven Development (TDD): TDD is highlighted as a strategy to write better tests by integrating testing into the development process from the start.
Summary of Contents
- Characteristics of Good Unit Tests: Discusses what makes a unit test effective, emphasizing the need for tests to validate behavior in detail and isolation.
- Examples of Poor vs. Improved Tests: Provides side-by-side comparisons of poor and improved test cases, showing how to refine tests to detect more issues.
- Test Driven Development (TDD): Explains the TDD process, offering practical advice on adopting it to write tests that enhance code quality and maintainability.
- Summary: Recaps the importance of early and isolated testing, and the value of good unit tests beyond mere code coverage.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 TDD Manifesto katas: Exercises to practice TDD techniques.
- 🔗 Kata-log katas: Additional katas to enhance TDD skills.
🔴 The Advanced Guide to UserDefaults in Swift
This blog post provides an in-depth exploration of UserDefaults in Swift, particularly with the enhancements introduced in Swift 5. The article guides readers on effectively using UserDefaults for small data storage and delves into its internal structure and performance considerations. It also covers advanced topics like designing type-safe key-value storage using property wrappers and observing changes in UserDefaults.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://www.vadimbulavin.com/advanced-guide-to-userdefaults-in-swift/
Published: December 9, 2019
Authors: Vadim Bulavin
Tags:
Swift, iOS, UserDefaults, Swift 5, Property Wrappers
Key Points
- UserDefaults Overview: Understand the use of UserDefaults for storing small data and the types of data it supports.
- Internal Structure: Explore how UserDefaults are stored as .plist files and the implications of this structure on performance.
- Advanced Implementation: Learn how to create type-safe key-value storage using property wrappers in Swift.
- Observing Changes: Implement mechanisms for observing changes in UserDefaults values using Key-Value Observing (KVO).
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: A brief overview of the evolution of UserDefaults in the context of Swift's development.
- UserDefaults Overview: Detailed discussion on what kind of data should be stored in UserDefaults and its internal implementation.
- Key-Value Storage Implementation: Step-by-step guide to implementing type-safe key-value storage using property wrappers.
- Observing UserDefaults: Techniques to observe changes in UserDefaults values, enhancing app responsiveness and data integrity.
- Conclusion: A recap of key insights about using UserDefaults effectively in modern Swift applications.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 The Complete Guide to Property Wrappers in Swift 5: A comprehensive guide to understanding and using property wrappers in Swift.
- 🔗 swift-corelibs-foundation: Explore the foundation source code for a deeper understanding of UserDefaults internals.
🔵 Writing Effective Release Notes: A Guide for Developers
Effective communication with your app's customers is essential. While many companies settle for generic phrases like "Bug fixes and performance improvements" in their release notes, writing great release notes doesn't need to be hard. Well-crafted release notes not only engage your users but also show your dedication to continually improving the app.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://blog.eliperkins.com/great-release-notes
Published: 2024-09-01
Authors: Eli Perkins
Tags:
release-notes, app-updates, customer-engagement
Key Points
- Writing release notes should focus on the customer rather than the company.
- Clear and consistent communication in release notes builds excitement and informs users of important changes.
- Avoid generic phrases; instead, highlight the benefits and outcomes of updates for the user.
Summary of Contents
-
Importance of Great Release Notes: Release notes are a direct line of communication with your users. Properly crafted notes can enhance user engagement and show that you value their experience.
-
Guidelines for Writing Release Notes:
- Naming & Capitalization: Follow consistent rules for naming and capitalizing features.
- Tone and Tense: Use an active voice, avoid unnecessary words like "now," and focus on the user's experience.
- What's New: Emphasize the outcomes and behavior changes brought by new features.
- Bug Fixes: Be concise, front-load the fixes, and focus on how the fixes affect the user.
-
Handling No User-Facing Changes: When no user-facing updates are available, it's okay to reuse previous release notes, especially for ongoing features. This keeps the communication relevant and consistent.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 GitHub's Brand Content Guidelines: Follow these guidelines for consistent naming and capitalization.
- 🔗 GitHub Voice & Tone Guidelines: Ensure your release notes align with the overall brand voice.
🔵 Adapter Design Pattern in iOS
The Adapter Design Pattern is a structural design pattern that enables objects with incompatible interfaces to collaborate by using an intermediary known as the Adapter. This pattern is highly valuable in iOS development, especially when integrating third-party libraries, adapting legacy code, or bridging different frameworks.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://blog.stackademic.com/adapter-design-pattern-in-ios-9e008ec29414
Published: 2023-11-07
Authors: Stackademic
Tags:
design-patterns, swift, ios-development, architecture, adapter-pattern
Key Points
- Definition: Allows incompatible interfaces to work together via a wrapper object.
- Core Components: Target, Adapter, Adaptee, and Client.
- Use Cases: Integrating third-party libraries, simplifying complex interfaces, and bridging frameworks.
- Advantages: Enhances modularity, reusability, and separation of concerns in code.
- Disadvantages: May increase complexity and dependency.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: Overview of the Adapter Pattern and its significance in iOS.
- Core Components Explained: Details of the pattern's four components (Target, Adapter, Adaptee, and Client).
- Examples:
- General Scenarios: Printed photographs to digital, train systems with different engines.
- iOS Specific: Wrapping third-party libraries, adapting APIs.
- Step-by-Step Implementation in Swift:
- Creating the Target interface.
- Implementing the Adaptee.
- Designing the Adapter.
- Using the Adapter in the Client.
- Advantages and Disadvantages: A balanced view of the pattern's trade-offs.
🔵 Facade Design Pattern in iOS
The Facade Design Pattern is a structural design pattern that provides a unified interface to a set of interfaces in a subsystem, simplifying the interaction with complex systems. In iOS development, it is often used to streamline access to subsystems like network, database, and view layers.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://medium.com/@omar.saibaa/facade-design-pattern-in-ios-52138dd70e46
Published: 2023-11-01
Authors: Omar Saibaa
Tags:
design-patterns, swift, ios-development, facade-pattern, architecture
Key Points
- Definition: Provides a simplified interface to complex subsystems.
- Use Cases: Frequently used in iOS apps for simplifying access to network layers, database interactions, or view components.
- Advantages: Simplifies client code, decouples interfaces, reduces complexity, and improves performance through abstraction and caching.
- Disadvantages: Can introduce additional complexity, abstraction penalties, and reduced flexibility in some cases.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: Overview of the Facade Pattern and its role in simplifying subsystems.
- Examples: Conceptual and real-world scenarios, such as:
- Restaurant menu as a façade for complex kitchen operations.
- Unified access to banking app subsystems for checking balances, transferring money, and deposits.
- Simplifying interactions in e-commerce apps like Amazon.
- Unified interfaces for Facebook-like apps managing network, database, and view layers.
- Implementation Steps: A step-by-step guide to identifying subsystems, defining simplified interfaces, and creating facade classes to delegate requests.
- Code Examples: Example implementations demonstrating the benefits of the pattern in various contexts.
- Advantages and Disadvantages: Highlights the trade-offs when using this pattern.
🔵 Flyweight Design Pattern in iOS
The Flyweight Design Pattern is a structural design pattern focused on reducing memory usage by sharing intrinsic states among multiple objects. This approach minimizes redundancy and optimizes resource management in applications.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://thekrazyjames.medium.com/flyweight-design-pattern-in-ios-e5666433cd08
Published: 2024-05-11
Authors: The Krazy James
Tags:
design-patterns, swift, ios-development, flyweight-pattern, memory-optimization
Key Points
- Definition: Reduces memory usage by sharing intrinsic (immutable) states among objects.
- Intrinsic State: Immutable properties like birthdate or nationality.
- Extrinsic State: Mutable properties like expiration date or address.
- Advantages: Saves memory usage by eliminating redundancy.
- Common Mistakes: Avoid multiple instances of the same intrinsic state; use a factory or singleton to enforce uniqueness.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: Overview of the Flyweight Pattern and its relevance in optimizing memory usage.
- Core Concepts: Explanation of intrinsic and extrinsic states with examples from a driver’s license and passport system.
- Implementation: A detailed breakdown of how to separate intrinsic and extrinsic states in Swift, with code examples.
- Common Mistakes: Highlights pitfalls such as duplicating intrinsic states and suggests solutions like factories or singletons.
- Conclusion: Discusses the pattern’s utility in scenarios like gaming, where shared textures reduce memory consumption.
Here is the blog post formatted strictly according to the blog_post.md template:
🔵 Composite Design Pattern in iOS
The Composite Design Pattern is a structural design pattern that allows the composition of objects into tree structures to represent part-whole hierarchies. This pattern simplifies client code by allowing uniform treatment of individual and composite objects.
Details
URL: 🔗 Original Blog Post
Published: [YYYY-MM-DD]
Authors: Abdulahd 1996
Tags:
design-patterns, swift, ios-development, composite-pattern, architecture
Key Points
- Definition: Represents part-whole hierarchies, enabling clients to treat individual objects and composites uniformly.
- Use Cases: Commonly used in file systems, GUI hierarchies, and analytics tracking in iOS.
- Advantages: Promotes scalability, abstraction, and separation of concerns.
- Real-World Examples: File systems, event tracking with multiple analytics services.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: Explanation of the Composite Pattern and its role in managing hierarchies.
- Example Implementation:
Component: The protocol defining the interface for bothLeafandCompositeobjects.Leaf: Simple objects likeTextFileandImageFile.Composite: Complex objects likeFolderaggregating both files and subfolders.
- Real-World iOS Use Case: Refactoring tightly coupled event tracking into a scalable design using
EventTrackerprotocol andCompositeTracker. - Code Examples: Step-by-step implementation in Swift for hierarchical object management.
- Advantages: Improves scalability, decouples client code, adheres to SOLID principles, and simplifies testing.
🔵 SwiftUI MVVM-C: A Real-World Guide
This article explores the implementation of the Model-View-ViewModel-Coordinator (MVVM-C) pattern in SwiftUI with a detailed, practical example. MVVM-C combines SwiftUI’s declarative syntax with a structured architectural approach, enabling scalable and maintainable app development.
Details
Authors: Swift and Beyond
Tags:
swiftui, mvvm-c, ios-development, app-architecture, navigation
Key Points
- Definition: MVVM-C is an architectural pattern that separates concerns into Models, Views, ViewModels, and Coordinators to manage complex navigation flows.
- Advantages:
- Simplifies navigation flows.
- Improves modularity, scalability, and maintainability.
- Ensures separation of concerns.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: Brief overview of the MVVM-C pattern and its importance in SwiftUI.
- Coordinator: Central navigation hub managing the navigation stack with
pushPage()andclearNavigationStack(). - ViewModels: Protocol-driven, reactive logic connecting the UI to the Coordinator.
- Views: Declarative SwiftUI components leveraging
@ObservedObjectfor state-driven UI updates. - Gender Entry Example: Demonstrates modular design using reusable components like
TextComponentandButtonComponentView. - Code Walkthrough: Full implementation of a SwiftUI app using MVVM-C, including reusable styles and navigation customization.
UML Class Diagram
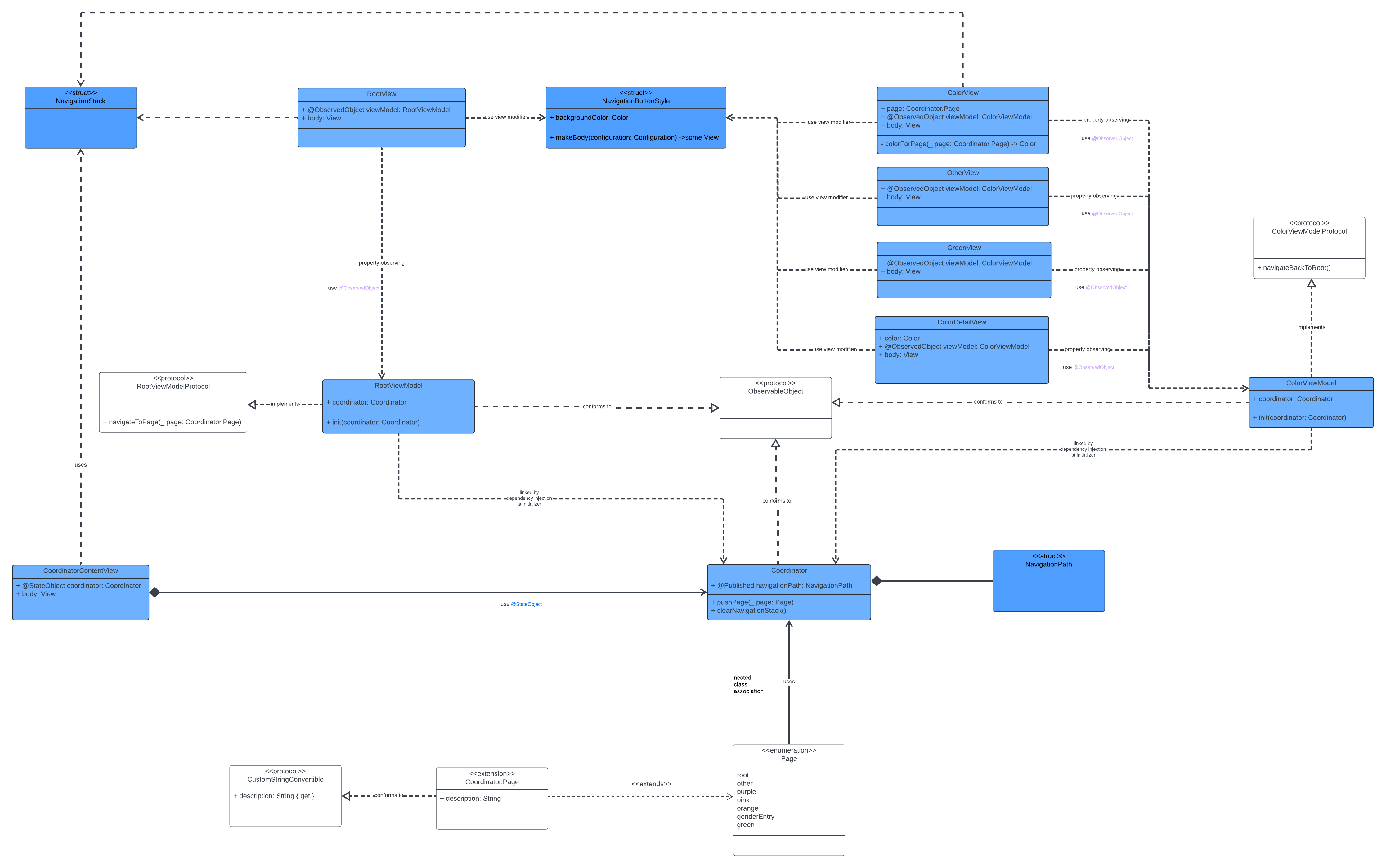
Helpful Links
🔵 How to Modularize a Monolithic iOS App
This blog post outlines a structured approach to transitioning from a monolithic iOS application to a modular architecture. By leveraging the principles of layered architecture and dependency inversion, it explains how to organize code into distinct modules for improved maintainability, scalability, and efficiency.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://vbat.dev/how-to-modularize-monolith-ios-app
Video: 🔗 Watch Here
Published: 2024-05-12
Authors: Vitaly Batrakov
Tags:
iOS Development, Modular Architecture, Dependency Injection, Layered Architecture
Key Points
- Modular Architecture:
- Divides an app into Core, Feature, and Composition Root layers.
- Promotes separation of concerns and loose coupling.
- Dependency Direction Rule: Dependencies can flow upwards but not downwards.
- Steps to Modularize:
- Begin by identifying and extracting shared functionalities into the Core Layer.
- Modularize feature-specific code into isolated Feature Modules.
- Use the Composition Root to manage dependency injection and object graph assembly.
- Best Practices:
- Avoid circular dependencies by inverting dependencies using protocols.
- Minimize direct dependencies between modules within the same layer.
Summary of Contents
- From Monolith to Modularization:
- Overview of monolithic and layered architectures.
- Introduction to dependency direction rules and the layered modular architecture.
- Core Layer:
- Contains shared functionalities like networking, logging, UI components, and analytics.
- Operates independently of other core modules.
- Feature Layer:
- Encapsulates feature-specific logic, UI, and data handling.
- Encourages independent development and reusability.
- Composition Root:
- Centralized location for dependency injection and assembling object graphs.
- Facilitates flexibility and maintainability.
- Common Dependency Scenarios:
- Handling dependencies across modules using dependency inversion.
- Strategies for managing upward, downward, and lateral dependencies.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 Modular App Example on GitHub: Explore a simple implementation of modular architecture.
- 🔗 Dependency Injection Guide: Learn about DI patterns in iOS.
- 🔗 Introducing the Composition Root Pattern: Insights into the composition root approach.
SwiftUI
🔵 Double Optional Bindings or Something idk
This article explores a SwiftUI pattern involving double optionals, used in a project to manage the state of a sheet that either creates a new item or edits an existing one. By using an optional of an optional type, the code can signal whether to show the sheet and whether the sheet is in creation or editing mode.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://phlippieb.dev/posts/double-optional-bindings/
Published: June 25, 2024
Authors: Phlippie Bosman
Tags:
Swift, SwiftUI, Optional, State Management
Key Points
- Double Optionals in SwiftUI: The article introduces a pattern where an optional of an optional type is used to control both the visibility and mode (create or edit) of a SwiftUI sheet.
- Use Case: This pattern is particularly useful in scenarios where a view needs to switch between creating a new item and editing an existing one.
- SwiftUI Integration: The pattern is integrated into SwiftUI using the
.sheet(item:)modifier, which automatically presents a view when the bound state is non-nil.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: The post begins by explaining the context in which the author discovered the double optional pattern while working on a SwiftUI app.
- Main Body: Detailed explanation of how the pattern works, including Swift code snippets that demonstrate the use of double optionals to manage sheet presentation and mode (create/edit).
- Conclusion: The article concludes with a reflection on the "freaky" nature of double optionals and their utility in SwiftUI for managing complex state scenarios.
Additional Resources
- SwiftUI Documentation: 🔗 SwiftUI Framework Documentation
- Optional Binding in Swift: 🔗 Understanding Optional Binding
🔵 Enhancements in Pulse 3.2: Advanced Search, List Management, and More
This blog post dives into the exciting new features introduced in Pulse version 3.2, focusing on the revamped search functionality, optimized list performance, and new tools for sorting and grouping logs. These enhancements, made possible by SwiftUI's .searchable modifier and other innovations, significantly improve the usability and efficiency of Pulse for iOS developers.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://kean.blog/post/pulse-search
Published: January 24, 2023
Authors: Alex Grebenyuk
Tags:
iOS, SwiftUI, Pulse, Search, UI Components
Key Points
- SwiftUI
.searchablemodifier: A powerful tool introduced in iOS 15, now enhanced with token support in iOS 16, streamlining the search experience in Pulse. - Optimized List Handling: Overcomes performance issues in List by limiting the displayed items and using dynamic loading as users scroll, ensuring smooth performance.
- Advanced Grouping and Sorting: New toolbar features allow for detailed grouping and sorting of logs, helping developers quickly find the information they need.
- Pinning for Quick Access: Reintroduced pins feature, allowing important logs to be pinned and easily accessed.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction to Pulse 3.2: Overview of the major updates, emphasizing the role of search and list management in improving user experience.
- Search Enhancements: Detailed look at how the
.searchablemodifier and tokenization enhance search capabilities. - Handling Large Lists: Explanation of the strategy used to optimize list performance, including the decision to revert to UITableView for heavy lifting.
- Grouping and Sorting: Insight into the new grouping and sorting functionalities, especially the “Group by Session” feature.
- Reintroduction of Pins: Description of the pins feature, highlighting its utility for developers.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 Apple’s “Adding Search to Your App”: Official documentation on the
.searchablemodifier. - 🔗 Pulse GitHub Repository: Access to the source code and further details about Pulse.
- 🔗 Regex Combinators: Background on the parser combinators used in Pulse’s search feature.
🔵 Understanding SwiftUI's PreferenceKeys
The article explains how the PreferenceKey protocol in SwiftUI allows child views to send values up the view hierarchy to parent views, which is the opposite of how Environment variables work, where data flows down the hierarchy. This technique is essential for cases where data needs to be passed upwards without relying on state variables or bindings.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://swiftlogic.io/posts/understanding-swiftui-preferencekeys/
Published: Jul 21, 2024
Authors: Osaretin Uyigue
Tags:
swift, swiftui, ios development, preference keys, data flow, data binding
Key Points
- PreferenceKey Protocol: Enables the upward flow of data in SwiftUI, contrary to the typical downward data flow.
- Custom
PreferenceKeys: Demonstrated with examples, allowing child views to communicate their heights to a parent view. - Real-World Use: Includes a practical example of a custom navigation title that leverages
PreferenceKeys.
Summary of Contents
- How it Works: An overview of how data typically flows in SwiftUI and how
PreferenceKeysinvert this flow. - How
PreferenceKeysWork: A breakdown of thePreferenceKeyprotocol and how it allows child views to send values upwards. - Creating a Custom
PreferenceKey: Step-by-step guide to creating a customPreferenceKeyto pass data up the view hierarchy. - Using
PreferenceKeysin Views: An example implementation showing how to usePreferenceKeysin child and parent views. - Real-World Use Case: A demonstration of using
PreferenceKeysto set a custom navigation title in a SwiftUI view.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 Leveraging ToolbarContentBuilder to Refactor Your SwiftUI Toolbar Code: Discusses the use of
ToolbarContentBuilder, another powerful tool in SwiftUI. - 🔗 How to Inject Dependencies into SwiftUI @StateObject: A tutorial on dependency injection with
@StateObjectin SwiftUI.
🔵 Customizing the Appearance of Symbol Images in SwiftUI
This blog post by Natalia Panferova provides a comprehensive guide on customizing SF Symbols in SwiftUI. The article covers essential techniques such as adjusting symbol size, color customization, rendering modes, variable values, and design variants to enhance the visual consistency and user experience in iOS apps. By following these methods, developers can create more intuitive and visually appealing interfaces.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://nilcoalescing.com/blog/CustomizingTheAppearanceOfSymbolImagesInSwiftUI/
Published: July 22, 2024
Authors: Natalia Panferova
Tags:
SwiftUI, iOS, SF Symbols, UI Design, Swift
Key Points
- Size Adjustment: Learn how to scale SF Symbols in SwiftUI by using the
**font()**and**imageScale()**modifiers. - Color Customization: Explore how to apply colors and gradients to symbols using the
**foregroundStyle()**modifier. - Rendering Modes: Understand different rendering modes like Monochrome, Hierarchical, Palette, and Multicolor, and how they impact symbol appearance.
- Variable Values: Discover how to dynamically change a symbol’s appearance based on state using variable values.
- Design Variants: Utilize design variants like fill and slash to communicate different states or actions in your UI.
Summary of Contents
- Size: Techniques for scaling and adjusting the weight of symbols in SwiftUI to ensure visual consistency.
- Color: Customizing symbol colors, including the use of gradients and other
**ShapeStyle**options. - Rendering Modes: Detailed explanation of different rendering modes and their practical applications in UI design.
- Variable Value: How to use variable values to represent dynamic states in your app, such as volume or battery level.
- Design Variants: Applying design variants like fill, slash, and enclosures to SF Symbols for enhanced UI clarity.
Additional Resources
- Enhanced replace transition for SF Symbols in iOS 18: 🔗 Learn more about advanced transitions for SF Symbols
- Reading and setting color scheme in SwiftUI: 🔗 Guide on handling color schemes in SwiftUI
🔵 How to Customise the SwiftUI List Style and Background Color
This article dives deep into customizing the appearance of SwiftUI List views. The tutorial covers how to adjust list background colors, modify separators, and use custom cells. With step-by-step examples, you’ll learn how to make your List views stand out with unique styles beyond the default options provided by SwiftUI. Whether you're new to SwiftUI or looking to refine your UI design skills, this guide is packed with practical tips and code snippets.
Details
Published: 2023-02-01
Authors: Karin Prater
Tags:
SwiftUI, iOS Development, UI Design, List Customization
Key Points
- Learn how to customize SwiftUI List styles, including background colors, separators, and insets.
- Practical code snippets for implementing unique list styles.
- Detailed examples of customizing list row height and modifying section headers and footers.
Summary of Contents
- Example Data Structure: Introduction to a custom
Foodstruct used throughout the examples. - Using a Custom Cell: How to create and implement custom cells in your List view.
- List Separators: Techniques for hiding and coloring row and section separators.
- List Row Size and Insets: Adjusting row height and modifying insets for a more polished look.
- Changing the SwiftUI List Background Color: Methods for changing both list and cell background colors.
- Extravagant Example: A showcase of the full range of customizations possible with SwiftUI Lists.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 SwiftUI List View: A Deep Dive into one of the most important components of SwiftUI.: A comprehensive guide to understanding SwiftUI List views.
- 🔗 SwiftUI Layout Cookbook: A free mini-book to master SwiftUI layouts.
🔵 Programmatically Trigger SwiftUI Actions
This article discusses five different methods to programmatically trigger actions in SwiftUI, focusing on the onChange operator introduced in SwiftUI 2.0. It explores options ranging from basic boolean state management to advanced techniques using Combine and @Published properties.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://betterprogramming.pub/programmatically-trigger-swiftui-actions-be2dcb8acf0d
Published: 2020-09-14
Authors: Mark Lucking
Tags:
SwiftUI, iOS Development, State Management, Swift
Key Points
- SwiftUI State Management: The article delves into various techniques for managing state and triggering UI changes in SwiftUI.
- onChange Operator: It highlights the new
onChangeoperator in SwiftUI 2.0 and its applications. - Advanced State Control: Options 4 and 5 demonstrate more advanced state management strategies using
@PublishedandCombine.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: Overview of the need for triggering actions in SwiftUI, especially with the advent of SwiftUI 2.0.
- Option 1: Simple boolean state control for toggling UI elements based on a timer.
- Option 2: Enhanced state control using
onAppearandonDisappearwith the id modifier for more responsive UI updates. - Option 3: Introduction of
onChangeto directly observe and react to state changes within a view. - Option 4: Using
@PublishedandObservableObjectto manage state across multiple views without tightly coupling them. - Option 5: Utilizing Combine’s
PassthroughSubjectfor even looser coupling and greater control over state-driven actions.
Additional Resources
- SwiftUI Documentation: 🔗 SwiftUI 2.0 Overview
- Combine Framework: 🔗 Introduction to Combine
🟢 ScrollPosition for ScrollView in iOS 17 and SwiftUI 5
This article discusses the new scrollPosition modifier in SwiftUI 5, introduced with iOS 17, which allows developers to control the initial scroll position within a ScrollView. The post includes code examples demonstrating how to implement this feature in various scenarios, such as creating a chat interface that starts at the bottom of the conversation.
Details
URL: 🔗 Link to the original blog post
Published: 2023-08-02
Authors: DevTechie
Tags:
SwiftUI, iOS Development, iOS 17, ScrollView, Swift
Key Points
- The
scrollPositionmodifier in SwiftUI 5 enables developers to set the initial scroll position in aScrollView. - It can be used to replicate UI patterns like starting a conversation view from the bottom, similar to Apple's Messages app.
- The modifier supports various anchor points such as
.top,.center, and.bottom, and it can be applied to both vertical and horizontal scrolls.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction to scrollPosition Modifier: This section introduces the
scrollPositionmodifier and its significance in controlling the scroll view's initial position. - Chat Interface Example: Detailed example of creating a chat interface where the scroll starts at the bottom, mimicking the behavior of messaging apps.
- Application in Horizontal Scroll: Discusses how to apply
scrollPositionto horizontal scrolls, including examples with images. - Advanced Use Cases: Explores other use cases, such as centering content in both horizontal and vertical scroll views.
Additional Resources
- SwiftUI Documentation: ��🔗 SwiftUI
ScrollViewdocumentation - iOS 17 Developer Preview: 🔗 Official Apple documentation for iOS 17
🟢 3 Ways to Share State in SwiftUI That You Need to Know
This blog post explores various strategies for sharing state between views in SwiftUI, highlighting common patterns and best practices. We will dive into techniques like using singletons, dependency injection, environment objects, and stores, providing code examples and discussing the pros and cons of each approach.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://dev.to/amodrono/3-ways-to-share-state-in-swiftui-that-you-need-to-know-1ink
Published: 2024-09-01
Authors: Amodrono
Tags:
SwiftUI, iOS, State Management, Dependency Injection, EnvironmentObject
Key Points
- Understanding different methods to share state between views in SwiftUI.
- Singleton patterns for global state access.
- Dependency injection to maintain loosely coupled components.
- Utilizing
@EnvironmentObjectfor shared data across multiple views. - Implementing stores to manage complex state across an application.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: A brief overview of the importance of state management in SwiftUI and why it’s crucial to have clean and maintainable code.
- Solution 1: Singletons: Discussion on the singleton pattern, its implementation in SwiftUI, and scenarios where it’s most appropriate.
- Solution 2: Dependency Injection: Explanation of dependency injection, with examples on how to pass view models down the view hierarchy.
- Using Environment Objects: Introduction to
@EnvironmentObjectand how it simplifies state management across multiple views. - Solution 3: Stores: Detailed look at using a store pattern, inspired by Redux, for managing complex state in SwiftUI applications.
- Conclusion: A summary of the best practices and recommendations for managing state in SwiftUI.
🔵 Global Sheets Pattern in SwiftUI
Managing sheet presentations in SwiftUI can become cumbersome, especially when scaling your app to include multiple sheets across different screens. This article introduces the Global Sheets Pattern, which simplifies sheet management by centralizing logic and streamlining code, making your app more maintainable and scalable.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://azamsharp.com/2024/08/18/global-sheets-pattern-swiftui.html
Published: 2023-09-18
Authors: AzamSharp
Tags:
SwiftUI, Swift, iOS, State Management, UI Patterns
Key Points
- The Global Sheets Pattern reduces redundancy by centralizing sheet management logic.
- Utilizing an enum-based approach simplifies the code for managing multiple sheets.
- Custom environment values offer flexibility in managing state and actions across different views.
- Simplified API ensures maintainable and scalable architecture for managing sheets.
Summary of Contents
- Displaying a Basic Sheet: Introduces the basics of using the
isPresentedargument in SwiftUI for sheet presentations. - Enum-Based Sheets: Shows how to encapsulate sheet types with an enum to simplify code when managing multiple sheets.
- Global Sheets: A more advanced pattern using custom environment values to globally manage sheets across an app.
- Handling OnDismiss: Adds the capability to handle sheet dismissal by introducing a second closure for the
onDismissevent. - Stacked Sheets: Briefly covers managing stacked sheets in specific cases where overlapping sheets are necessary.
Additional Resources
- SwiftUI Documentation: Official SwiftUI documentation on 🔗 sheet view modifiers.
- AzamSharp SwiftUI Courses: 🔗 AzamSharp School offers more resources on iOS development and workshops.
🚀 Mastering SwiftUI Navigation with Coordinators
Discover how to overcome SwiftUI’s navigation limitations and build scalable, production-ready apps by integrating UIKit’s Coordinator pattern into your projects.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://blog.jacobstechtavern.com/p/swiftui-apps-at-scale
Authors: Jacob’s Tech Tavern
Tags:
swiftui, navigation, coordinator-pattern, ios-development, uikit
Key Points
- SwiftUI Navigation Challenge: SwiftUI tightly couples navigation logic with views, hindering scalability and testability.
- Coordinator Pattern Solution: Leverage the Coordinator pattern to decouple navigation from views, enabling a scalable and testable architecture.
- Hybrid Approach: Combine the declarative power of SwiftUI with UIKit’s mature navigation system for seamless interoperability.
Summary of Contents
- SwiftUI’s Evolution and Limitations: A brief history of SwiftUI’s growth and its navigation challenges in complex apps.
- The Navigation Problem: An in-depth explanation of why SwiftUI’s built-in navigation APIs fall short for large-scale apps.
- The Coordinator Pattern: Step-by-step implementation of the Coordinator pattern to encapsulate navigation logic, using examples such as
AppCoordinatorandNavigationContext. - Integration with UIKit: Techniques for wrapping SwiftUI views in
UIHostingControllerand usingUINavigationControllerfor seamless integration. - Enhanced Control: Advanced customizations using subclassed
UIHostingControllerfor styling and lifecycle management.
Helpful Links
🟢 Mastering TextEditor in SwiftUI
SwiftUI's TextEditor is a powerful tool for building editable text views, offering a variety of customization options to meet different requirements. This article explores its core functionality, from basic configurations to advanced features like text selection, focus management, character limits, and writing tools. We'll also examine alternatives and strategies for enhancing its capabilities.
Details
URL: 🔗 Mastering TextEditor in SwiftUI
Published: 2024-11-17
Authors: Artem Novichkov
Tags:
SwiftUI, TextEditor, text editing, iOS development, writing tools
Key Points
- Basic Setup:
TextEditorrequires aBinding<String>and supports customization for fonts, colors, and line spacing. - Focus Management: Use the
focusedmodifier to control the appearance of the keyboard dynamically. - Advanced Features: Add find-and-replace functionality, customize writing tools, and handle text selection for complex editing needs.
- Character Limit Enforcement: Implement character limits using modifiers like
onChange. - Alternatives: Explore
TextField,UITextView, or third-party frameworks for specialized use cases.
Summary of Contents
- Basic Requirements: Focus management, character limits, and reading vs. editing modes are essential for robust text editing.
- Configuration Options: Customize
TextEditorwith features like autocorrection control, background styling, and keyboard configuration. - Focus and Interaction: Learn how to manage focus and hide/show the keyboard as required.
- Advanced Modifiers: Enable find-and-replace capabilities, writing tools, and introspection for read-only mode.
- Alternatives: Consider using
UITextView,TextFieldwith vertical axis support, or third-party frameworks like 🔗 RichTextKit.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 TextEditorExample Repository: Final example code for mastering
TextEditor. - 🔗 SwiftUI Documentation: Official Apple documentation on
TextEditor. - 🔗 RichTextKit: A third-party framework for rich text editing in SwiftUI.
🔴 Deep Dive Into Environment in SwiftUI
SwiftUI’s @Environment tools provide a powerful mechanism for managing shared state across an application. This article delves into the concepts, best practices, and new features like @Observable and @Bindable introduced in iOS 17, ensuring that developers can build scalable and maintainable applications.
Details
URL: 🔗 Deep Dive Into Environment in SwiftUI
Published: 2024-11-18
Authors: AzamSharp
Tags:
SwiftUI, @Environment, @EnvironmentObject, state management, iOS development
Key Points
@EnvironmentObjectBasics: UseObservableObjectto inject global state into a SwiftUI hierarchy.- Efficient State Updates: SwiftUI uses re-evaluation and diffing to optimize performance.
- iOS 17 Enhancements: The
@Observablemacro simplifies global state management with automatic property publication. - Real-World Use Cases: Manage global or context-specific states cleanly for modular and testable components.
Summary of Contents
- Environment in SwiftUI: Overview of how
@Environmentenables seamless shared state management. - Re-Evaluation vs. Re-Rendering: Insights into SwiftUI’s diffing mechanism to optimize updates.
- New Features in iOS 17: Explore
@Observableand@Bindablemacros for cleaner and faster state handling. - Best Practices: Avoid tight coupling, inject dependencies based on context, and pass only necessary data to child views.
- Real-World Applications: Example scenarios like shopping carts and multi-tab apps to demonstrate modular design.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 SwiftUI Documentation: Official Apple documentation on SwiftUI’s
@Environment. - 🔗 HelloMarket Repository: Open-source shopping cart app using
@Environment. - 🔗 Full-Stack E-commerce Course: Learn how to build scalable applications from scratch.
🔴 Refactor SwiftUI Navigation Layer Using Coordinator Pattern
This article explores the evolution of SwiftUI navigation design by refactoring a simple Router-based approach into a more robust Coordinator-based pattern. The new implementation supports stacked navigation, sheets, and full-screen covers, making it suitable for complex, scalable applications.
Details
URL: 🔗 SwiftUI Refactor Navigation Layer Using Coordinator Pattern
Published: 2024-11-17
Authors: Tiago Henriques
Tags:
SwiftUI, Coordinator Pattern, Navigation, iOS Development, Best Practices
Key Points
- Coordinator vs. Router: Coordinators manage navigation flows across multiple screens, enabling hierarchical and modular navigation patterns.
- New Features: Adds support for sheet and full-screen cover navigation with a custom
Routableprotocol. - Decoupled Design: Separates navigation logic from views, promoting clean architecture and scalability.
- Advanced Usage: Implements nested Coordinators for managing complex navigation flows (e.g., embedding a Favourites Coordinator within an App Coordinator).
Summary of Contents
- Router vs. Coordinator: Highlights the difference in scope and functionality between the two patterns.
- Coordinator Implementation: Introduces a
Routableprotocol and a customCoordinatorclass for managing various navigation types. - CoordinatorStack View: A generic solution for integrating stacked navigation, sheets, and full-screen covers in one component.
- Nested Coordinators: Demonstrates embedding child Coordinators within a parent Coordinator for modular navigation flows.
- Integration with Views: Uses
@Environmentto access Coordinators and manage navigation dynamically.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 Coordinators & SwiftUI: A deep dive into using Coordinators with SwiftUI.
- 🔗 Mastering iOS Navigation: Detailed guide on navigation strategies for iOS.
- 🔗 Coordinator Pattern in SwiftUI: Best practices for implementing Coordinators.
🟢 Implementing the "Shared With You" Feature in iOS Apps
This article walks you through implementing the Shared with You feature in iOS apps, introduced in iOS 16. It covers the feature's purpose, setup, and code implementation, making it easier for developers to integrate shareable content support in their apps.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://digitalbunker.dev/shared-with-you/
Published: 2024-11-19
Authors: Aryaman Sharda
Tags:
iOS Development, Swift, iOS Features, User Experience, Code Implementation
Key Points
- Purpose of "Shared With You": Aims to help users rediscover shared content like links, songs, and recommendations directly in the relevant apps.
- Setup Requirements: Universal Links must be configured, and testing should be done on physical devices.
- Core Components:
- Shelf: A prioritized list of shared content, arranged by system recommendations, pinned messages, and chronological order.
- Attribution View: Displays details about the shared content, including the sender and a link back to the original message.
Summary of Contents
- Getting Started: Explains prerequisites like enabling Universal Links and testing on physical devices.
- Implementation: Step-by-step guidance on integrating the
SWHighlightCenterclass to manage shared links and using theSWAttributionViewfor attribution display. - Customization: Examples of adding actions to the attribution view's context menu.
- Testing Tips: Key steps to ensure seamless testing of the feature.
- Final Code Example: Demonstrates creating a shelf UI in SwiftUI using
SharedWithYouService.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 Universal Link Testing Tool: A utility to verify and debug Universal Links.
- 🔗 Aryaman Sharda’s YouTube Channel: Tutorials on iOS development.
🟢 Using ViewThatFits to Create a More Accessible List Cell in SwiftUI
This article explores leveraging SwiftUI's ViewThatFits component to design list cells that adapt their layout based on available screen space or text size. The approach enhances accessibility and maintains scalability for future updates.
Details
Published: 2024-11-20
Authors: Stackademic
Tags:
SwiftUI, Accessibility, List Cell, ViewThatFits, Responsive Design
Key Points
- Dynamic Layout Switching: Demonstrates how
ViewThatFitsautomatically switches between horizontal and vertical layouts. - Customizable Accessibility: Scales effortlessly for different screen sizes and text accessibility settings.
- Minimal Complexity: Simplifies layout logic without resorting to conditionals or manual calculations.
- Scalability: Prepares apps for future changes in Apple’s UI framework.
Summary of Contents
- The Problem: Designers often require list cells that adapt seamlessly to different font sizes or screen orientations.
- Horizontal and Vertical Layouts: Examples of
HStackandVStackimplementations for responsive layouts. - Using
ViewThatFits: Explanation of how the component tests view sizes and displays the first fitting layout, with a focus on the.horizontaldirection for optimization. - Sample Implementation: Code examples show a list of adaptable cells using
ViewThatFitswithHorizontalViewandVerticalView.
Additional Resources
- Explore More Articles by the Author: 🔗 Stackademic on Medium
- Apps Built with Native Development: 🔗 JPMTech Portfolio
🔴 Mastering SwiftUI Performance
This article delves into SwiftUI performance optimization, exploring techniques to enhance rendering efficiency and manage view updates more effectively. Readers will learn about strategies like custom diffing, efficient data model design, minimizing dependencies, and utilizing debugging tools.
Details
URL: 🔗 Mastering SwiftUI Performance
Published: 2024-11-20
Authors: YourCoachMaz
Tags:
SwiftUI, Performance Optimization, Diffing, Efficient Data Models, Swift Programming
Key Points
- SwiftUI Diffing: Understand how SwiftUI updates affected views efficiently using a diffing algorithm.
- Custom Diffing: Utilize
EquatableViewand.equatable()for tailored view updates. - Efficient Data Models: Prefer structs over classes for faster stack allocation and immutability.
- Lazy Loading: Optimize lists with
LazyVStackand similar constructs for better memory management. - Debugging Tools: Leverage SwiftUI Profiler and
Self._printChanges()for insights into unnecessary view updates.
Summary of Contents
- Understanding Diffing in SwiftUI: Overview of SwiftUI's diffing algorithm and its limitations for complex hierarchies.
- Using EquatableView for Custom Diffing: How to implement custom update logic by conforming to
Equatableand wrapping views. - Efficient Data Models and Dependencies: Guidance on using structs, enums, and property wrappers like
@Stateand@ObservedObject. - Optimizing View Rendering: Techniques such as lazy loading, minimizing conditional logic, and avoiding redundant computations.
- Debugging and Profiling: Tools and practices to identify and resolve performance bottlenecks in SwiftUI projects.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 SwiftUI Docs: Apple’s official documentation on SwiftUI.
- 🔗 Profiling SwiftUI: Watch WWDC videos on SwiftUI performance optimization.
🔴 Behind the Scenes of UI Part 2: SwiftUI
This blog post dives deep into SwiftUI, Apple’s declarative framework for building user interfaces. While emphasizing its declarative and data-driven nature, the article explores how SwiftUI operates under the hood by comparing it to UIKit and shedding light on its internal processes.
Details
URL: 🔗 Behind the Scenes of UI Part 2: SwiftUI
Published: [Add Publish Date]
Authors: [Author's Name]
Tags:
[SwiftUI], [UIKit], [iOS Development], [Declarative UI], [Frameworks]
Key Points
-
SwiftUI: A Declarative Framework
SwiftUI allows developers to describe the desired UI and behavior, and the framework manages the rendering process. -
Data-Driven Approach
UI changes automatically reflect data or state modifications, simplifying synchronization. -
Integration with UIKit
SwiftUI uses UIKit, Core Animation, and Core Graphics behind the scenes for rendering and animations, ensuring compatibility and leveraging proven technologies. -
The Role of the
body
A SwiftUI view'sbodydefines both layout and content. Re-evaluating thebodyis central to rendering updates.
Summary of Contents
-
Understanding the View and Render Tree
Explains how SwiftUI employs an ephemeral view tree (structs) and a persistent render tree (attribute graph) for state tracking and efficient updates. -
Phases of the SwiftUI Render Loop
The render loop is dissected into evaluation, layout, and rendering phases, each playing a crucial role in UI updates. -
Connection with UIKit and CATransaction
Highlights how SwiftUI relies on UIKit's core principles, including CATransactions, for managing the render process. -
Hosting Views
Discusses_UIHostingView, which bridges SwiftUI views with UIKit, showcasing how views map to UIKit components. -
Challenges and Future Possibilities
Explores the challenges developers face when transitioning from UIKit to SwiftUI and how Apple might evolve SwiftUI in the future.
Additional Resources
- Video: 🔗 Watch the accompanying video.
- Related Blog: 🔗 SwiftUI Layout System by Alex Grebenyuk.
🔵 SwiftUI Craftsmanship: Mastering ViewModifiers
SwiftUI's ViewModifiers empower developers to refine views with precision, allowing for enhanced styling, behavior, and layout. This article delves into the types, best practices, and common pitfalls of using ViewModifiers, comparing their role to the finishing touches of a master craftsman.
Details
URL: 🔗 SwiftUI Craftsmanship: ViewModifiers
Published: 2024-11-11
Authors: Captain SwiftUI
Tags:
SwiftUI, iOS Development, ViewModifiers, UI Design, Best Practices
Key Points
- ViewModifiers act like a craftsman's finishing touches, refining views without altering their core structure.
- Custom modifiers encapsulate frequently used design elements, improving reusability and consistency.
- The order of modifiers affects visual layout and behavior significantly.
- Using categories of modifiers like Styling, Layout, and Event simplifies design decision-making.
- Thoughtful application of modifiers improves readability, performance, and accessibility.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction to ViewModifiers: A comparison of ViewModifiers to woodworking techniques, emphasizing their role in enhancing views.
- Categories of Modifiers: Styling, Event, Functional, Behavior, Layout, and Visibility Modifiers, explained with practical examples.
- Best Practices: Includes logical stacking, reusability, and accessibility considerations.
- Common Pitfalls: Performance issues, complex logic within modifiers, and layout missteps.
Additional Resources
- Apple Documentation: 🔗 SwiftUI ViewModifiers
🔵 Defining Custom Environment Values in SwiftUI
SwiftUI allows developers to pass data between views using @Environment. While the predefined EnvironmentValues offer a robust set of tools, this article explores creating custom environment values, empowering developers to introduce and manage their own keys and values for view hierarchies.
Details
URL: 🔗 How to Define Custom Environment Values in SwiftUI
Published: 2021-08-30
Authors: Sarun W.
Tags:
SwiftUI, Environment, Custom Keys, iOS Development, View Management
Key Points
- SwiftUI uses
@Environmentto pass data down a view hierarchy. - Developers can create custom environment keys and values using
EnvironmentKeyandEnvironmentValues. - Adding a dedicated modifier simplifies usage and improves readability.
- Custom environment values help encapsulate context-specific logic.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: Overview of
@Environmentand its potential for customization. - Step 1: Define a new environment key by conforming to
EnvironmentKeyand providing a default value. - Step 2: Extend
EnvironmentValuesto integrate the custom key. - Step 3: (Optional) Add a dedicated modifier for better usability.
- Demo: Example implementation with a sensitive data toggle for redacting sensitive information.
- Conclusion: Recap of the process and its benefits.
Additional Resources
- Apple Documentation: 🔗 Environment in SwiftUI
- Sarun's Guide to Environment: 🔗 What is @Environment in SwiftUI
🔴 Init to Win It: Understanding Initializers in SwiftUI
SwiftUI simplifies creating user interfaces, often making it unnecessary to define custom initializers. However, this simplicity can lead to misconceptions about when and why to use initializers. This article explores initializers in SwiftUI, focusing on their role, the nuances of property wrappers, and the complexities of working with StateObject and Observable.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://captainswiftui.substack.com/p/init-to-win-it
Published: 2024-08-28
Authors: Captain SwiftUI
Tags:
SwiftUI, iOS Development, Initializers, StateObject, Observable
Key Points
- Initializers establish initial property states and dependencies for SwiftUI views.
- Swift structs offer Memberwise Initializers by default, reducing boilerplate.
- Property Wrappers like
@Stateand@StateObjectbehave differently under the hood, requiring careful use in initializers. - Apple recommends specific practices for
StateObjectto ensure stability across redraws. - The newer Observation framework introduces
@Bindableand tracking without wrappers, simplifying some use cases.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction to Initializers: Overview of their purpose and role in SwiftUI's lifecycle.
- Property Wrappers: Insights into
@State,@Binding, and@StateObject, with examples and limitations. - StateObject Gotchas: Explanation of why
StateObjectinitializers require care and Apple's recommendations. - Observation Framework: Discussion on new approaches with
@State,@Bindable, and unwrapped Observables. - Best Practices: Tips for when to use Memberwise Initializers, custom initializers, or task modifiers.
Additional Resources
- Apple Documentation: 🔗 StateObject Initialization
- Property Wrappers Proposal: 🔗 Swift Evolution Proposal
- ObservableObject Differences: 🔗 StateObject vs ObservedObject
🔵 SwiftUI Craftsmanship: Designing Effective View Contracts
SwiftUI's flexibility allows developers to create dynamic UIs effortlessly. However, poor planning around a View's contract can lead to redundant code and limited reusability. This article explores View contracts in SwiftUI, focusing on crafting effective interfaces and asking the crucial question: "What is this View for?"
Details
URL: 🔗 SwiftUI Craftsmanship: View Contracts
Published: 2024-10-24
Authors: Captain SwiftUI
Tags:
SwiftUI, View Design, Reusability, UI Development, Best Practices
Key Points
- A View contract defines the data and functionality a View relies on.
- Asking "What is this View for?" ensures better planning and prevents short-sighted designs.
- Avoid locking Views to specific data types; instead, focus on the properties they display.
- Design FeatureViews as the entry point for feature hierarchies, handling core data requirements.
- Be cautious with
Environmentusage—it simplifies access but adds maintenance challenges.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction to View Contracts: Overview of how poor contracts limit flexibility.
- Case Study: Refactoring a
RowItemView to accept generic properties instead of rigid types. - FeatureViews: Explanation of top-level Views managing feature-specific data.
- Best Practices for Subviews: Balancing generic contracts with type-specific logic.
- Avoiding Pitfalls with Environment: When and how to use Environment responsibly.
Additional Resources
- Apple Documentation: 🔗 SwiftUI Views
- Related Article: 🔗 SwiftUI Craftsmanship: ViewModifiers
🔵 Full Disclosure: Mastering SwiftUI’s DisclosureGroup
The DisclosureGroup is one of SwiftUI's simplest yet most versatile components, allowing content to expand and collapse dynamically. While it’s great for providing additional information or controls on demand, this article dives deeper into customizing and rethinking its behavior, including creating a "drawer" that expands upwards.
Details
URL: 🔗 Full DisclosureGroup
Published: 2024-09-09
Authors: Captain SwiftUI
Tags:
SwiftUI, DisclosureGroup, Component Composition, UI Customization, Best Practices
Key Points
- DisclosureGroup Basics: A simple-to-implement component that provides toggled visibility for additional content.
- Customization with DisclosureGroupStyle: By modifying its style, DisclosureGroup can take on new forms, such as expanding upwards.
- Core Principles of SwiftUI Composition: Components should prioritize functionality over presentation, with styles enhancing the user experience.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction to DisclosureGroup: Overview of its interface and default behavior.
- Basic Usage: How to implement a DisclosureGroup with a label and content.
- Customization with Styles: Redefining DisclosureGroup behavior using
DisclosureGroupStyle, including flipping the label and content positions. - Practical Applications: Examples such as shopping cart displays and expanding drawers.
- Lessons in Composition: The importance of designing components with a functionality-first approach and leveraging styles for aesthetic adjustments.
Additional Resources
- Apple Documentation: 🔗 DisclosureGroup
- Related Article: 🔗 SwiftUI Craftsmanship: View Contracts
🔵 Dependency Injection in SwiftUI: Constructor vs Environment Injection
Dependency Injection (DI) is a crucial design pattern for building scalable and maintainable iOS applications. In SwiftUI, DI adopts a slightly different approach compared to UIKit. This article explores two key methods for implementing DI in SwiftUI: Constructor Injection and Environment Injection.
Details
URL: 🔗 DI in SwiftUI
Published: 2024-07-01
Authors: vbat.dev
Tags:
SwiftUI, Dependency Injection, @Environment, @EnvironmentObject, iOS Development
Key Points
- Constructor Injection: Dependencies are passed directly via initializers, maintaining familiarity with UIKit practices.
- Environment Injection: Dependencies are injected into the view hierarchy for access by child views.
- @EnvironmentObject: Injects an
ObservableObjectfor use in complex hierarchies. - @Environment: Uses a key/value approach to inject dependencies, suitable for both value and reference types.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction to Dependency Injection in SwiftUI: Overview of DI and its adaptation to SwiftUI.
- Constructor Injection: A familiar pattern extended to SwiftUI views.
- Environment Injection:
- @EnvironmentObject: For injecting
ObservableObjectinstances into the view hierarchy. - @Environment: For injecting key/value dependencies with safety and flexibility.
- @EnvironmentObject: For injecting
- Practical Examples: Demonstrations of each approach with code.
- Comparison and Best Practices: Discusses when to use
@EnvironmentObjectversus@Environmentfor injecting dependencies.
Additional Resources
- Apple Documentation: 🔗 EnvironmentValues
- Related Article: 🔗 DI in iOS: Complete Guide
UIKit
🔴 Behind the Scenes of UI: Part 1 - UIKit
This article explores the intricacies of UIKit, diving deep into how UIKit manages user interface updates and animations under the hood. By understanding these internal processes, developers can better optimize performance and troubleshoot UI-related issues. The article provides a detailed walkthrough of key concepts like Runloops, CoreAnimation, and CATransaction, making it invaluable for intermediate and advanced iOS developers.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://vbat.dev/behind-the-scenes-of-ui-part-1-uikit
Published: 2024-02-19
Authors: Vitaly Batrakov
Tags:
UIKit, CoreAnimation, Runloop, iOS Development, Advanced UI
Key Points
- Delves into the UI update process in UIKit, emphasizing Runloops and CoreAnimation.
- Explains CATransaction and its role in grouping UI updates.
- Discusses implicit vs explicit transactions and their implications on rendering.
- Introduces the Render Server, providing a clear understanding of inter-process rendering.
Summary of Contents
- Intro: Introduction to why understanding UIKit's internal processes is beneficial for developers.
- UIApplicationMain: Describes the entry point of an iOS app and its connection to Runloop.
- Runloop: Explains how Runloop handles events, including GCD main queue blocks and timers.
- CoreAnimation: Details the relationship between UIView and CALayer, along with layer trees.
- CATransaction: Discusses implicit and explicit CATransactions and their role in rendering updates.
- Render Server: Explains how rendering is handled in a separate process for better performance.
Additional Resources
- Apple Documentation on Runloops: 🔗 Runloop Overview
- Core Animation Guide: 🔗 Core Animation Basics
- Advanced Reading on Transactions: 🔗 Understanding CATransaction
🔵 Adapting UIHostingController to Changes in SwiftUI View Size
This article explores how to effectively use UIHostingController to bridge UIKit and SwiftUI in your projects. It highlights common pitfalls, discusses the correct approach to manage sizing options, and addresses challenges with integrating UIHostingController in various scenarios, such as popovers or legacy UIView-based systems.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://vbat.dev/adapting-uihostingcontroller-to-changes-in-swiftui-view-size
Published: 2024-03-30
Authors: Vitaly Batrakov
Tags:
SwiftUI, UIHostingController, UIKit Integration, Sizing Options, iOS Development
Key Points
- UIHostingController acts as a bridge between UIKit and SwiftUI, managing the SwiftUI view hierarchy in a UIKit environment.
- Improperly managing UIHostingController (e.g., not retaining it) can lead to issues like size changes not being reflected.
- With sizingOptions introduced in iOS 16, developers can handle dynamic sizing of SwiftUI views seamlessly, leveraging
.intrinsicContentSizeand.preferredContentSize. - The correct usage involves embedding UIHostingController as a child view controller to ensure proper lifecycle and sizing updates.
- For iOS versions prior to 16, manual approaches like
setNeedsUpdateConstraintsorinvalidateIntrinsicContentSizecan be used.
Summary of Contents
- Common Pitfalls:
- Issues with deallocating UIHostingController and the impact on size updates.
- Incorrect usage patterns, such as treating UIHostingController as a simple subview.
- iOS 16+ Features:
- Leveraging
sizingOptionsfor dynamic resizing with.intrinsicContentSizeand.preferredContentSize. - The importance of embedding UIHostingController as a child view controller.
- Leveraging
- Support for Older iOS Versions:
- Strategies for handling sizing in iOS 15 or earlier, using manual size updates.
- Workarounds for integrating SwiftUI in legacy UIView-based systems.
- Popover Integration:
- Challenges with preferredContentSize in popovers and solutions to improve animations and dynamic size updates.
Additional Resources
🔵 Safely Extending Legacy Code: A Swift Approach Using Protocols, Mocking, and Unit Testing
Refactoring legacy code is often necessary for improving maintainability and adding new features without disrupting existing functionality. This article demonstrates how to refactor a tightly coupled LegacyCode class using protocols, mocking, and unit testing, culminating in the addition of database-saving functionality.
Details
Published: 2024-05-12
Authors: Islam Moussa
Tags:
Swift, Refactoring, Unit Testing, Protocols, Legacy Code
Key Points
- Refactoring legacy code often involves addressing tight coupling and lack of modularity.
- Using protocols for dependency injection improves testability and flexibility.
- Mocks are essential for isolating core logic during testing.
- A structured approach to refactoring allows for seamless feature additions.
Summary of Contents
- Identifying Issues in Legacy Code: Highlights problems such as tight coupling, singleton dependencies, and poor testability.
- Protocol-Based Refactoring: Introduces modularity by wrapping dependencies like
LoggerandAPIServicein protocols. - Unit Testing with Mocks: Demonstrates the creation of mock services for isolating and testing functionality.
- Adding Database Functionality: Implements an in-memory database and integrates it with the refactored
LegacyCodeclass. - Ensuring Robustness Through Tests: Adds comprehensive unit tests to validate both existing and new functionality.
Additional Resources
🔵 Mastering Animations with CATransaction in Swift
Core Animation powers the smooth, polished animations you see in iOS and macOS. While UIView.animate() simplifies animation for most use cases, more complex motions require deeper understanding and tools like CATransaction. This article explores how CATransaction enhances your animation control, allowing fine-tuned synchronization and customization.
Details
URL: 🔗 Better iOS Animations with CATransaction
Published: 2017-06-01
Authors: Jon Cardasis
Tags:
iOS Development, Core Animation, CATransaction, CABasicAnimation, Swift
Key Points
- Core Animation Basics: Understand the dual-layer architecture: model layer for static values and presentation layer for animated states.
- CABasicAnimation: A versatile tool for animating
CALayerproperties, complementingUIView.animate(). - CATransaction: A grouping mechanism that synchronizes multiple animations across views and layers.
- Custom Timing Functions: Use CATransaction to define precise bezier curves for animation timing.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction to Core Animation: Explanation of how
CALayerpowers animations and the difference between view and layer animations. - CABasicAnimation Usage: Step-by-step guide to animating layer properties like
cornerRadiususing CABasicAnimation. - CATransaction Basics:
- Group animations to ensure synchronization.
- Control animation duration and timing across multiple animations.
- Combining CATransaction with UIKit and Core Animation: Example of coordinating
UIView.animate()andCABasicAnimationwith CATransaction. - Advanced Techniques: Custom timing functions using
CAMediaTimingFunctionfor precise bezier animation curves. - Practical Example: Real-world implementation of animating a UIButton’s size and corner radius simultaneously.
Additional Resources
- GitHub Project: 🔗 Better Animations Playground
- Apple Documentation: 🔗 Core Animation
- Related Topics: 🔗 CABasicAnimation Essentials
Xcode and Workflow
🟢 Multi-Cursor Editing in Xcode
Multi-cursor editing is a powerful feature in Xcode that allows developers to place multiple cursors in their code simultaneously, enabling efficient editing across multiple lines or sections. This feature is particularly useful for repetitive tasks such as renaming variables or adjusting code structures. The blog post explores different methods to activate and utilize multi-cursor editing, provides practical examples, and highlights the benefits of incorporating this feature into your workflow.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://sarunw.com/posts/multi-cursor-editing-in-xcode/
Published: November 11, 2020
Authors: Sarun Wongpatcharapakorn
Tags:
Xcode, Workflow, iOS Development
Key Points
- Efficient Code Editing: Multi-cursor editing speeds up code modifications by allowing simultaneous changes across multiple locations.
- Practical Use Cases: Useful in tasks like initializing custom coding keys and changing method parameter indentation styles.
- Easy to Use: Multiple methods to enable and disable cursors, making it adaptable to different coding styles.
Summary of Contents
- What is a Cursor? A brief explanation of what a cursor is in the context of code editing.
- What is Multi-Cursor Editing? Introduction to multi-cursor editing, its purpose, and how it can enhance coding efficiency.
- How to Use It? Step-by-step instructions on various methods to enable and manage multiple cursors, including using clicks, arrow keys, and dragging.
- Why Do We Need This? Discussion on the advantages of multi-cursor editing, supported by practical examples.
Additional Resources
- Add custom SwiftUI view to View Library with LibraryContentProvider: A guide on how to add custom SwiftUI views to Xcode’s view library.
- Useful Xcode shortcuts for unit testing: A compilation of handy Xcode shortcuts that streamline unit testing processes.
- How to create a macOS app without storyboard or xib files: Instructions on building macOS apps without relying on storyboards or xib files.
🔵 Using @DebugDescription in Xcode 16
Learn how to enhance debugging in Swift by utilizing the CustomDebugStringConvertible protocol and the new @DebugDescription macro introduced in Xcode 16. This article guides you through customizing debug outputs, ensuring clearer and more informative insights during development. Whether you're working with complex custom types or just aiming for more readable debugging information, these tools can significantly streamline your workflow.
Details
URL: 🔗 Original Blog Post
Published: July 21, 2024
Authors: Aryaman Sharda
Tags:
Xcode, Swift, Debugging, CustomDebugStringConvertible, @DebugDescription
Key Points
- The
CustomDebugStringConvertibleprotocol allows developers to customize the debug output of custom types, providing more detailed and readable information. - The new
@DebugDescriptionmacro in Xcode 16 improves the quality of life by integrating custom debug descriptions directly into Xcode's Variable Inspector and crash logs. - Developers using older versions of Xcode can still achieve similar functionality through LLDB Type Summaries and
.lldbinitconfigurations.
Summary of Contents
- Using CustomDebugStringConvertible: An introduction to the protocol, its implementation, and the benefits of customizing debug output.
@DebugDescriptionMacro: A detailed look at the new macro, how it works, and how it enhances the debugging experience in Xcode 16.- Macro Alternatives: Alternatives for developers who cannot upgrade to Xcode 16, focusing on LLDB Type Summaries and
.lldbinitconfigurations.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 LLDB Type Summary Documentation: Overview of how LLDB Type Summaries work.
- 🔗 Pitch: Debug Description Macro - Swift Forums: Discussion on the development and evolution of the
@DebugDescriptionmacro. - 🔗 Swift Debugging Tips: Tips and tricks for efficient debugging in Swift.
🔵 Testing Remote Push Notifications on iOS Simulator with Xcode 11.4+
With the release of Xcode 11.4, Apple introduced the ability to simulate remote push notifications in the iOS simulator, making testing easier without the need for physical devices. This update provides two ways to simulate push notifications: via the command line and by drag-and-drop using an .apns file.
Details
URL: 🔗 Apple Documentation – Creating the Remote Notification Payload
Published: 2024-09-13
Authors: ioswift.dev Team
Tags:
remote-notifications, Swift, iOS, Xcode, simctl
Key Points
- Simulating Notifications: Xcode 11.4 introduces the ability to simulate push notifications on the iOS simulator.
- Testing Methods: Two ways to test notifications—via command line and by drag-and-drop.
- Payload Format: Requires a valid APNS payload in JSON format, which can be referenced from Apple’s official documentation.
Summary of Contents
-
Creating the APNS Payload:
- An example of an APNS payload that can be used for testing remote notifications.
-
Testing via Command Line:
simctl pushcommand: A step-by-step guide on how to use thesimctlcommand to simulate push notifications on a running simulator.
-
Drag-and-Drop Method:
- A simple method where developers can drag-and-drop the
.apnsfile onto the simulator.
- A simple method where developers can drag-and-drop the
-
Troubleshooting:
- Common issues with payload files and how to ensure they contain the
Simulator Target Bundlekey.
- Common issues with payload files and how to ensure they contain the
Additional Resources
- 🔗 Apple Documentation – Creating the Notification Payload: Learn how to structure your APNS payload.
- 🔗 Xcode 11.4 Beta Release Notes: Official release notes detailing the new features of Xcode 11.4.
🔵 Automate Code Signing with Fastlane Match
Code signing is a critical step in app development for Apple platforms, ensuring apps are authorized and secure. This article introduces code signing concepts, such as provisioning profiles and signing certificates, and explains how to automate the process using Fastlane Match. This tool simplifies code signing, especially for teams, by centralizing and managing signing identities.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://www.polpiella.dev/automate-code-signing-with-fastlane-match/
Published: November 8, 2024
Authors: Pol Piella
Tags:
Fastlane, Code Signing, CI/CD, iOS Development, Provisioning Profiles
Key Points
- Provisioning Profiles:
- Define app permissions, including device access and entitlements.
- Bundle information to identify the app, its allowed devices, and signing certificates.
- Signing Certificates:
- Verify the developer’s identity and protect the app from tampering.
- Fastlane Match:
- Centralizes code signing by sharing identities via an encrypted repository.
- Works seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines, enabling automated signing.
Summary of Contents
- What Are Provisioning Profiles?
- Details the role of provisioning profiles in app authorization.
- What Are Signing Certificates?
- Explains how certificates authenticate developers and ensure app integrity.
- Managing Code Signing:
- Compares Xcode's automatic management with scalable team-oriented solutions.
- Using Fastlane Match:
- Step-by-step setup for initializing Fastlane Match with Git as storage.
- Generating and syncing signing identities for app development and distribution.
- CI/CD Code Signing:
- Instructions for configuring Fastlane Match in CI/CD pipelines using environment variables.
Additional Resources
Localization
🔵 Using XMLParser and NSAttributedString for Rich Text Formatting in Localizable Strings
This blog post discusses various methods for handling rich text formatting in localizable strings within iOS development. The author critiques common practices such as concatenated strings, substring lookups, and HTML-based formatting, highlighting their drawbacks in terms of translation accuracy and performance. The post concludes by proposing a more efficient solution using XML parsing to handle basic formatting with NSAttributedString.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://kean.blog/post/formatted-strings
Published: Nov 29, 2020
Authors: Alex Grebenyuk
Tags:
localization, iOS, NSAttributedString, XMLParser, performance
Key Points
- Concatenated Strings: This method is error-prone, particularly in maintaining correct word order for translations. It assumes a fixed sentence structure, which may not hold across different languages.
- Substring Lookup: While better than concatenation, this approach can fail when a substring appears multiple times, leading to potential translation and formatting issues.
- HTML for Formatting: Although HTML provides more control, it is slow and can introduce unnecessary complexity. The author mentions performance concerns, especially on devices like the iPhone 11 Pro.
- Proposed XML Parsing Solution: The author suggests using XMLParser to handle rich text formatting in localizable strings. This method is described as being faster and more reliable than HTML-based formatting, particularly for iOS applications.
Summary of Contents
- Poor Practices: The author discusses the issues with concatenated strings and substring lookup methods, explaining how these practices can lead to significant translation and performance challenges.
- HTML-Based Formatting: The blog explores the use of HTML for rich text formatting, noting its limitations in terms of performance and the extra effort required to maintain proper styling.
- Proposed XML Parsing Solution: The main highlight of the article is the author's proposed solution using XML parsing to apply text attributes. This method is described as being faster and more reliable than HTML-based formatting, particularly for iOS applications.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 10 Common Mistakes in Software Localization and How to Avoid Them: An article discussing common pitfalls in localization and strategies to avoid them.
- 🔗 Hacking with Swift: How to Convert HTML to an NSAttributedString: A guide on converting HTML to NSAttributedString in Swift.
🟢 Unleashing Global Reach: A Comprehensive Guide to Effortless iOS App Localization Using Google Sheets
This article provides a detailed walkthrough of iOS app localization, showcasing how to utilize Localizable.strings for translation and implement efficient workflows using Google Sheets and the gspread Python library. Aimed at developers looking to streamline localization processes, it introduces step-by-step instructions, structured strategies, and automation techniques to make your iOS app globally accessible.
Details
URL: 🔗 Unleashing Global Reach: A Comprehensive Guide
Published: 2024-01-17
Authors: Vinodh
Tags:
localization, ios-development, google-sheets, gspread, automation
Key Points
- iOS localization uses
Localizable.stringsfiles to manage translations effectively. - Google Sheets enhances collaboration by centralizing translation management.
- The gspread library automates the extraction of translations into app-compatible files.
- The guide highlights coding best practices for seamless integration and testing.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: Emphasizes the importance of app localization in today's global market.
- Implementing Localization in Xcode: Detailed instructions for creating and managing
Localizable.stringsfiles. - Google Sheets Integration: Tips for structuring Google Sheets for effective translation workflows.
- Python Automation with gspread: Step-by-step guide to setting up, authenticating, and using gspread for exporting translations.
- Benefits and Challenges: Highlights the advantages of using centralized systems and the pitfalls of manual processes.
- Code Examples: Includes Python scripts for automation and Swift examples for integrating translations.
Additional Resources
- Apple Developer Localization Guide: 🔗 Link to Apple's official documentation
- gspread Documentation: 🔗 gspread API Reference
🟢 iOS Localization Tutorial in SwiftUI Using String Catalog
This tutorial walks you through iOS localization in SwiftUI, highlighting the advantages of String Catalogs in Xcode 15+. It covers step-by-step instructions to localize text and elements, including app display names and permission request messages. This guide ensures that your app feels natural, respectful, and culturally adapted for a global audience.
Details
URL: 🔗 iOS Localization Tutorial in SwiftUI Using String Catalog
Published: 2024-01-06
Authors: hyleedevelop
Tags:
localization, swiftui, string-catalog, ios-development, xcode15
Key Points
- Localization is more than translation; it adapts apps to cultural and regional specifics.
- String Catalogs simplify the localization process in Xcode 15+ with automated string extraction.
- The guide includes methods for handling singular and plural strings and localizing Info.plist keys.
- Demonstrates localization of permission messages using
NSUserTrackingUsageDescription.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction to Localization: Definition and importance of localization for user inclusivity.
- Setting Up Localization in SwiftUI:
- Creating projects with SwiftUI.
- Adding new languages and building the project to auto-populate the String Catalog.
- Working with String Catalogs:
- Advantages of String Catalogs over legacy Strings files.
- Managing pluralized strings with examples.
- Testing Localization: Steps to change the language settings on simulators and real devices.
- Localizing Info.plist:
- Display names using
CFBundleDisplayName. - Permission request messages using
NSUserTrackingUsageDescription.
- Display names using
- Conclusion: Encouragement to embrace localization for a better global reach and user experience.
Additional Resources
- Apple Localization Documentation: 🔗 Localization Guide
- GitHub Repository: 🔗 Localization Tutorial Code
🔵 iOS Localization: LocalizedStringResource vs. LocalizedStringKey vs. String
This article examines Apple's localization types in SwiftUI—LocalizedStringResource, LocalizedStringKey, and String—to evaluate their strengths, limitations, and applicability. It provides an in-depth comparison to help developers choose the right approach for their apps.
Details
URL: 🔗 iOS Localization: LocalizedStringResource vs. LocalizedStringKey vs. String
Published: 20244-09-16
Authors: Nick McConnel
Tags:
localization, localizedstringresource, swiftui, ios-development, string-management
Key Points
- LocalizedStringResource is Apple’s recommended type for representing localizable strings.
- LocalizedStringKey integrates well with SwiftUI but has modular and backend string challenges.
- String with
String(localized:)offers flexibility and consistency but lacks type safety. - Modularization and consistent language lookup are critical factors in choosing the right approach.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: Discusses the evolution from
NSLocalizedStringto newer types likeLocalizedStringResource. - LocalizedStringKey:
- Well-suited for SwiftUI.
- Challenges include modularization and handling backend-localized strings.
- Summary: Good for simpler setups but struggles with comments, modules, and backend integration.
- LocalizedStringResource:
- Groups localization details like keys, default values, comments, and bundles into one type.
- Handles modular setups but has issues with consistent language lookup and SwiftUI integration.
- Summary: Excellent for modularity but problematic for certain localization workflows.
- String with
String(localized:):- Integrates cleanly with SwiftUI and modular codebases.
- Handles backend-localized strings and maintains consistent language lookup.
- Summary: Flexible but lacks type safety for enforcing localization.
- Conclusion: Encourages a nuanced approach based on app complexity and modular requirements. Advocates for String(localized:) in most cases due to its balance of integration and reliability.
Additional Resources
- WWDC 2023 Localization Video: 🔗 Strings Catalog and Localization
- Apple Documentation: 🔗 LocalizedStringResource Reference
Concurrency
🔵 Closures vs. Combine vs. Async-Await in Swift: A Comprehensive Comparison
Explore the evolution of asynchronous coding methods in Swift, from closures to the Combine framework and the powerful Async-Await introduced in Swift 5.5. This comparison highlights the pros and cons of each method and how they have transformed Swift development.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://medium.com/@GetInRhythm/closures-vs-combine-vs-async-await-993eb1da4d44
Published: 2024-09-15
Authors: Mike Adams
Tags:
swift, async-await, closures, combine, asynchronous programming, ios development
Key Points
- Swift offers three primary methods for asynchronous coding: Closures, Combine, and Async-Await.
- Closures allow for flexible and customizable asynchronous operations but can lead to complex code structures, particularly with callback hell.
- Combine simplifies handling asynchronous data streams and offers a declarative approach, making it a powerful framework for reactive programming.
- Async-Await introduces a more readable, synchronous-looking syntax for asynchronous tasks, improving code clarity and reducing complexity.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: Overview of the three asynchronous coding methods and their respective introductions in Swift.
- Closures: Discusses closures as a versatile and foundational feature for asynchronous coding in Swift, particularly useful for handling network requests and UI updates.
- Combine: Covers the reactive programming approach of Combine, including its key components (publishers and subscribers) and use cases like data stream management and asynchronous event handling.
- Async-Await: Highlights Async-Await as a modern, language-level feature that simplifies asynchronous code, using familiar keywords like
awaitandasyncto enhance readability and reduce callback complexity. - Comparison of Code Examples: Visual side-by-side comparison of closures, Combine, and Async-Await in terms of readability, complexity, and code maintainability.
- Resources: Additional reading materials for deeper insights into Combine and Async-Await.
🔵 Swift Async-Await Explained: Simplifying Asynchronous Programming
Discover the magic of Swift’s async-await, a powerful tool introduced in Swift 5.5 that simplifies asynchronous programming by eliminating callback complexity. This article explores how async-await works, its benefits, and how to implement it effectively in real-world scenarios.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://www.dhiwise.com/post/swift-async-await-explained-simplifying-asynchronous
Published: 2024-08-04
Authors: DhiWise Team
Tags:
swift, async-await, asynchronous programming, ios development, concurrency, swift 5.5
Key Points
- Async-await in Swift significantly improves code readability and maintainability compared to older callback-based methods.
- Handling errors in asynchronous functions becomes more consistent and robust with
async throwsandawait. - Swift’s concurrency model ensures efficient task management and structured concurrency, reducing the risk of common multi-threading issues.
Summary of Contents
- Why Concurrency Matters: Describes the importance of concurrency for modern apps and the limitations of traditional approaches.
- Swift’s Asynchronous Evolution: Explores the shift from completion handlers and GCD to the more streamlined async-await syntax.
- The Game-Changer: Async Await: Provides an overview of how async-await simplifies asynchronous tasks by allowing non-blocking, sequential code execution.
- Understanding Swift Async-Await: Delves into the key concepts, such as
asyncfunctions, theawaitkeyword, and the difference between synchronous and asynchronous calls. - Simplification of Asynchronous Code: Compares the readability and maintainability of async-await versus older callback methods.
- Handling Errors in Async-Await: Demonstrates how error handling is managed seamlessly in Swift's asynchronous code.
- Integration with Swift Concurrency Model: Explains how async-await interacts with Swift’s broader concurrency features, including
TaskandTaskGroup. - When to Use and Not to Use Async-Await: Offers practical advice on when to apply async-await and when to stick with traditional approaches for optimal performance.
Additional Resources
- Swift Async Await vs. Combine: A guide on how to choose between Swift async-await and the Combine framework for different use cases.
- Async Let vs. Await in Swift: Discusses the benefits of
async letfor initiating concurrent tasks compared to directawaitusage. - withCheckedThrowingContinuation: Explores how to bridge callback-based APIs with async-await using continuations.
🔴 Advanced Swift Actors: Re-Entrancy & Authentication
Actors are a powerful tool in Swift for writing asynchronous, thread-safe code, but they are not without their complexities. In this article, we take a deep dive into actor re-entrancy and its implications when building an authentication service for iOS apps. Through sequence diagrams, real-world examples, and in-depth code demonstrations, you’ll learn how to use actors to solve common concurrency issues while optimizing network performance.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://blog.jacobstechtavern.com/p/advanced-swift-actors-re-entrancy
Published: 2024-09-10
Authors: Jacob’s Tech Tavern
Tags:
Swift, Actors, Concurrency, iOS Development, Re-entrancy, OAuth 2.0
Key Points
- Actors and Re-Entrancy: Explanation of how actors enforce serial execution but allow interleaving of tasks, causing potential re-entrancy issues.
- Authentication Service Use Case: A real-world example using OAuth 2.0 to build a token-based authentication system that avoids unnecessary concurrent token refreshes.
- Handling Multiple Requests: Optimization techniques using actors to prevent duplicated API calls and improve network efficiency by ensuring only one token refresh at a time.
- Concurrency Theory: A detailed breakdown of Swift’s concurrency model, including cooperative threading, tasks, and how actors use serial executors to manage state safely.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction to Actors: The basics of actors in Swift, how they work, and why they are useful for concurrency.
- Real-Life Use Case: Implementing a simple authentication service with token refresh logic, demonstrating the potential for re-entrancy issues with concurrent requests.
- Optimizing Authentication Logic: A step-by-step guide to improving the authentication service by leveraging actor-based concurrency to ensure a single token refresh across multiple requests.
- Swift Concurrency Runtime: A deep dive into how Swift’s concurrency model works under the hood, including task execution, suspension points, and actor serial queues.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 OAuth 2.0 Standard: Learn more about OAuth 2.0, the most common authentication protocol used in mobile apps.
- 🔗 Swift Actors Documentation: Apple’s official documentation on actors and concurrency in Swift.
🔵 Understanding the Actor Reentrancy Problem in Swift
Swift actors have brought significant improvements to handling asynchronous code, eliminating data races and deadlocks. However, actors are not free from threading issues, and a common problem developers face is actor reentrancy. In this post, we’ll walk through what the reentrancy problem is, why it’s problematic, and how to prevent it when using actors in Swift.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://swiftsenpai.com/swift/actor-reentrancy-problem/
Published: 2024-09-10
Authors: Swift Senpai
Tags:
Swift, Actors, Concurrency, Reentrancy, Async
Key Points
- Actors in Swift: Actors allow developers to write asynchronous code that’s free from data races and deadlocks.
- Reentrancy Problem: The actor reentrancy problem arises when an actor is interrupted during its execution, leading to inconsistent state changes.
- Preventing Reentrancy: Developers can mitigate reentrancy issues by performing state mutations in synchronous code or checking the actor’s state after suspension points.
Summary of Contents
- Real-life Example of Reentrancy: A
BankAccountactor with asynchronous withdrawals shows how concurrent withdrawals can lead to negative balances due to reentrancy. - Identifying the Problem: The issue occurs when the actor state (account balance) changes between suspension points during concurrent transactions.
- Solutions to Prevent Reentrancy: Two main approaches are highlighted: performing state mutations in synchronous code and checking actor state after suspension points.
- Thread Safety vs. Reentrancy: The distinction between thread safety and reentrancy is explored, showing how actors guarantee thread safety but do not inherently protect against reentrancy issues.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 Preventing Data Races with Actors: Learn how actors help prevent data races.
- 🔗 Sendable in Swift: Using
Sendableto further enhance concurrency safety. - 🔗 Swift Concurrency Basics: Introduction to Swift concurrency.
🔴 Async Await in Swift: The Full Toolkit
This blog post, authored by Jacob Bartlett and published on July 22, 2024, provides a comprehensive overview of the various tools available in Swift Concurrency. It explains how to use async/await, async let, Tasks, Task groups, Actors, MainActor, Sendable, Continuations, AsyncSequence, AsyncStream, and Async Algorithms, emphasizing both theory and practical application. The article is particularly valuable for developers looking to deepen their understanding of Swift Concurrency and apply it effectively in their projects.
Details
URL: 🔗 Async await in Swift: The Full Toolkit
Published: July 22, 2024
Authors: Jacob Bartlett
Tags:
Swift Concurrency, async/await, Actors, Task Groups, Swift
Key Points
- Understanding async/await: Learn the fundamental syntax and how to efficiently manage asynchronous tasks in Swift.
- Advanced Concurrency Techniques: Explore the use of async let, Task groups, and Actors to enhance performance and safety in concurrent operations.
- Practical Examples: The post includes code snippets that illustrate the correct usage of each concurrency tool in real-world scenarios.
- Avoiding Common Pitfalls: Guidance on how to prevent common issues like data races and performance bottlenecks using Swift Concurrency features.
Summary of Contents
- async / await: Introduction to the basic building blocks of Swift Concurrency and how to utilize them for efficient task management.
- async let: Explanation of how to perform multiple asynchronous operations in parallel, avoiding bottlenecks in sequential code execution.
- Task and Task Group: Detailed discussion on structured and unstructured concurrency, including the use of task hierarchies and cancellation.
- Actors and MainActor: Exploration of how Actors ensure thread-safe operations and how MainActor is used for UI updates.
- Sendable and Continuations: Insight into preventing data races at compile-time and bridging legacy APIs with modern Swift Concurrency.
- AsyncSequence and AsyncStream: Overview of asynchronous sequences and streams, and their integration with Combine and other Swift features.
- Async Algorithms: Introduction to the Async Algorithms package, which extends the capabilities of AsyncSequence for more complex data processing.
Additional Resources
- Advanced Swift Actors: Re-entrancy & Interleaving: 🔗 Read more
- Swift Algorithms GitHub Repository: 🔗 Visit Repository
🔵 Guide to Multi-Threading with GCD in iOS
This article explores how Grand Central Dispatch (GCD) can be leveraged to implement multi-threading in iOS applications, enabling concurrent and parallel execution of tasks for optimal performance.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://betterprogramming.pub/guide-to-multi-threading-gcd-83009f5d62cb
Authors: Neel Bakshi
Tags:
multi-threading, ios, swift, gcd, performance, dispatchqueues
Key Points
- Multi-threading in iOS: Achieved using threads, Grand Central Dispatch (GCD), or
OperationQueues. - Concurrency vs. Parallelism:
- Concurrency: Time-sliced task execution giving the illusion of parallelism.
- Parallelism: True simultaneous execution across CPU cores.
- GCD Overview: Provides tools to manage task execution on serial or concurrent queues.
Summary of Contents
- Queues: Fundamental components in GCD:
- Serial Queues: Process tasks sequentially in a FIFO manner.
- Concurrent Queues: Handle multiple tasks concurrently or in parallel.
- Executing Tasks: Differences between
async(non-blocking) andsync(blocking) task submissions. - Dispatch Groups: A tool to coordinate the completion of multiple tasks.
- Race Conditions: Problems arising from concurrent resource access and their solutions:
- Serial Queues
- Locks and Semaphores
- Barriers
Helpful Links
🔴 Problematic Patterns in Swift Concurrency
This blog post outlines common patterns in Swift concurrency that can lead to complications. While "best practices" are subjective and context-dependent, the author identifies recurring issues worth avoiding.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://www.massicotte.org/problematic-patterns
Published: 2024-11-19
Authors: Matt Massicotte
Tags: Swift, Concurrency, Best Practices, Code Patterns
Key Points
- Split Isolation: Mixing isolation domains in a single type can create unexpected limitations and confusion.
- Task.detached Misuse: Overused for convenience but has side effects like losing inherited priorities and task-local values.
- Explicit Priorities: Explicitly setting priorities can lead to unintended performance issues and priority inversions.
- MainActor.run Overuse: Often unnecessary; prefer leveraging Swift's built-in actor isolation mechanisms.
- Stateless Actors: Avoid actors without mutable state unless there's a compelling reason.
- @preconcurrency Import Risks: Can inadvertently introduce warnings or semantic issues when adapting completion handlers.
- Redundant Sendable Conformance: Global actor-isolated types are inherently
Sendable, so additional conformance may indicate misunderstanding. - RunLoop APIs: Limited compatibility with non-MainActor contexts; require careful handling.
- Blocking Async Work: Using synchronous constructs like
DispatchSemaphorerisks deadlocks. - Unstructured Concurrency: Prefer structured concurrency for clarity, maintainability, and implicit cancellation support.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: A reflection on the pitfalls of “best practices” in emerging technologies like Swift concurrency.
- Common Problematic Patterns: Detailed analysis of specific issues with examples and solutions.
- Final Thoughts: Encourages experimentation while being mindful of the trade-offs and dangers of blindly following advice.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 Step-by-Step Network Request
- 🔗 Dynamic Isolation with MainActor
- 🔗 Reliably Testing Async Code in Swift
🔵 The Full Toolkit for Swift Concurrency: Async/Await
Mastering Swift Concurrency is essential for iOS developers working on modern, responsive apps. This blog post covers the wide array of tools in Swift Concurrency, such as async/await, Task, Task Group, and Actors, while exploring when and why you might use them. It provides not just theoretical insights but also practical examples to deepen your understanding.
Details
URL: ��🔗 https://www.emergetools.com/blog/posts/swift-async-await-the-full-toolkit#the-toolkit
Published: 2024-07-22
Authors: EmergeTools
Tags:
Swift Concurrency, iOS Development, Actors, async/await, Task Group
Key Points
- async/await: Provides syntactic sugar for writing asynchronous code, suspending execution at suspension points for efficiency.
- async let: Enables parallel execution of multiple asynchronous operations to minimize bottlenecks.
- Task: The fundamental building block of concurrency, supporting unstructured asynchronous work.
- Task Groups: Facilitates concurrent execution of a dynamic number of tasks, with flexible error handling.
- Actors: Ensures safe concurrent access to mutable state.
- MainActor: A concurrency construct designed for UI work to ensure updates happen on the main thread.
- Sendable: A protocol for marking data as safe to share across concurrency contexts.
- Continuations: Bridges closure-based legacy APIs with Swift’s modern concurrency model.
- AsyncSequence: Provides iterable async collections for sequential, asynchronous value processing.
- AsyncStream: Extends AsyncSequence to handle continuous value emission, useful for multi-callback APIs.
- Async Algorithms: An external package providing tools like
debounce,zip, andremoveDuplicatesto create pipelines for async sequences.
Summary of Contents
- The Toolkit:
- Highlights tools such as
async/await,Task, andActors, focusing on their use cases.
- Highlights tools such as
- Code Examples:
- Includes parallelization with
async let, error handling with Task Groups, and bridging legacy APIs with continuations.
- Includes parallelization with
- Advanced Topics:
- Delves into Actors' re-entrancy, MainActor's thread safety, and the role of
Sendablein preventing data races.
- Delves into Actors' re-entrancy, MainActor's thread safety, and the role of
- Best Practices:
- Discusses patterns like cooperative cancellation, combining async sequences, and integrating
Async Algorithmsfor real-time data processing.
- Discusses patterns like cooperative cancellation, combining async sequences, and integrating
Additional Resources
Here’s the blog post formatted according to the blog_post.md template:
🔵 Advanced Swift Actors: Re-Entrancy and Interleaving
Actors in Swift provide a powerful tool for managing concurrency, enforcing serial access to state and methods. However, the nuances of actor behavior, especially re-entrancy and interleaving, can lead to unexpected results if not well understood. This blog explores these concepts with a practical example of building an optimal authentication service.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://blog.jacobstechtavern.com/p/advanced-swift-actors-re-entrancy
Published: 2023-10-10
Authors: Jacob’s Tech Tavern
Tags:
Swift Concurrency, Actors, iOS Development, Authentication, Concurrency
Key Points
- Actors in Swift: Reference-typed entities ensuring serial access, backed by a
SerialExecutor. - Re-Entrancy: An actor's async method can suspend at
await, allowing interleaving of other tasks. - Authentication Example:
- Naïve implementation results in redundant work and API calls.
- Optimized version uses Tasks and re-entrancy to handle multiple concurrent token refresh requests efficiently.
- Practical Tips:
- Use
Taskas a property to manage concurrent requests for shared resources. - Leverage actor's isolation to synchronize access to shared state.
- Use
Summary of Contents
- Introduction to Actors:
- Explanation of serial access and interleaving.
- Importance of actors in managing state in concurrent contexts.
- Authentication Service Use Case:
- Common authentication workflow (OAuth 2.0).
- Problems in naïve implementation with concurrent token refresh.
- Theory: Swift Concurrency Model:
- Cooperative threading model.
- Role of continuations and executors.
- Optimizing the AuthService:
- Implementation of
Taskproperty to synchronize token refresh requests. - Step-by-step breakdown of interleaving behavior and caching.
- Implementation of
Additional Resources
🔵 Is Dynamic Isolation in Swift Concurrency Bad?
Dynamic isolation in Swift concurrency is a nuanced tool. While static isolation is often preferred for its safety and clarity, dynamic isolation remains an essential escape hatch. This article explores the trade-offs between the two approaches, explains when and why you might use dynamic isolation, and provides practical examples.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://www.massicotte.org/dynamic-isolation
Published: 2024-11-24
Authors: Matt Massicotte
Tags:
Swift Concurrency, MainActor, Static Isolation, Dynamic Isolation
Key Points
- Static Isolation is enforced by the compiler, offering safety and clarity.
- Dynamic Isolation provides runtime flexibility for legacy or complex codebases.
- Incremental Adoption of concurrency often requires dynamic isolation.
- Atomicity in
MainActor.runcan simplify complex thread-safe operations.
Summary of Contents
- Static Isolation: Explains
@MainActorand other type-level annotations for compiler-enforced thread safety. - Dynamic Isolation in Practice: Details runtime constructs like
MainActor.runand their use cases. - When to Choose Dynamic Isolation: Discusses incremental concurrency adoption and maintaining atomicity.
- Best Practices: Suggests when and how to transition from dynamic to static isolation for long-term maintainability.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 Rob Napier’s Gist on Atomicity: A deeper dive into atomic operations using
MainActor.run. - 🔗 Intro to Isolation: Foundational concepts in Swift isolation.
🔵 Understanding Actor Isolation in Swift
Actor isolation is at the heart of Swift’s concurrency model, aiming to eliminate data races. While it introduces new concepts, many mechanisms behind isolation are familiar. This blog breaks down the key ideas behind actor isolation, making it approachable even for developers new to Swift concurrency.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://www.massicotte.org/intro-to-isolation
Published: 2024-11-24
Authors: Matt Massicotte
Tags:
Swift Concurrency, Actor Isolation, Static Isolation, Dynamic Isolation
Key Points
- Isolation in Swift eliminates data races, ensuring safe access to mutable state.
- Definitions Govern Isolation: Isolation is always determined at compile time by type or function definitions.
- Three Isolation Types:
- None (default),
- Static (e.g.,
@MainActor), - Dynamic (
MainActor.assumeIsolated).
- Opting Out: Use
nonisolatedto remove isolation from functions or constants. - Closures and Protocols: Inherited isolation and protocol-based isolation can influence design patterns.
- Dynamic Isolation for Legacy Code: Useful for pre-concurrency systems where static isolation is impractical.
- Practical Implications: Understanding isolation is crucial when working with SwiftUI or adopting concurrency incrementally.
Summary of Contents
- What is Isolation?: Explains how Swift eliminates data races and enforces thread safety.
- Understanding Definitions: Highlights how to analyze isolation based on type and function definitions.
- Types of Isolation: Breaks down static and dynamic isolation mechanisms, including examples.
- Closures and Inherited Isolation: Discusses how closures adopt isolation from their surrounding context.
- Protocols and Isolation: Explains how protocol isolation affects design.
- Dynamic Isolation: Demonstrates how to bridge gaps in legacy code or systems with runtime isolation guarantees.
- SwiftUI Challenges: Examines how SwiftUI’s inconsistent isolation model creates practical issues.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 Swift Concurrency Recipes: Techniques for working with isolation and protocols.
- 🔗 Complete Concurrency Checking: How to enable warnings for incomplete concurrency isolation.
- 🔗 Swift Evolution Proposal 0420: Recent changes improving isolation in Swift.
Design
🔵 The Sound of Software
Sound in software is often overlooked, yet it plays a crucial role in creating engaging and immersive user experiences. This article explores the art and science of sound design in software, offering guidelines on when to use sound, how to design it effectively, and how to implement it in your apps. With practical examples and techniques, it shows how sound can transform mundane software interactions into something much more meaningful.
Details
URL: 🔗 Read Full Article
Published: April 25, 2024
Authors: Andy & Thomas Williams
Tags:
sound-design, software-design, user-experience, UI/UX, audio
Key Points
- Strategic Use of Sound: Sound should be used to communicate important actions, enhance moments, and create a sense of tangibility in software.
- Designing Sound: Good sound design involves breaking repetition through variation, layering sounds for depth, and creating a coherent soundscape.
- Implementation Techniques: Consider device settings, provide user control, and pair sound with haptics to create a more immersive experience.
Summary of Contents
- When to Use Sound: Guidelines on where sound adds value, such as communicating actions or adding "juice" to key moments.
- Designing Sound: Techniques like breaking repetition with variation, layering sounds, and building a coherent sound world.
- Implementing Sound: Practical tips for sound implementation, including overriding sound settings, pairing with haptics, and designing for target devices.
- How to Start: Advice for beginners, from getting and editing sounds to hiring a sound designer.
Additional Resources
- !Boring Sound Kit: A collection of sounds used in !Boring apps to help you get started.
- Meta Sound Kit: A sound kit from Meta for prototyping.
- Designing Sound (WWDC '17): An Apple video on sound design.
🔵 iPhone 16 Screen Sizes: What Developers Need to Know
Apple's iPhone 16 lineup introduces new screen sizes and features for the Pro models while maintaining support for older devices. Here's a detailed overview of the changes and implications for developers.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://useyourloaf.com/blog/iphone-16-screen-sizes/
Published: 2024-11-19
Authors: Keith Harrison
Tags: iOS Development, Screen Sizes, UIKit, SwiftUI, Responsive Design
Key Points
- New Screen Sizes: iPhone 16 Pro (6.3") and Pro Max (6.9") models feature larger displays with smaller bezels.
- Base Models Consistency: iPhone 16 and 16 Plus retain 6.1" and 6.7" displays, respectively, like their predecessors.
- Pro Enhancements: Pro models feature titanium bodies, Always-On display, ProMotion, and support for USB 3 transfer speeds.
- Screen Brightness Updates: All models now offer a 1-nit minimum brightness for improved viewing in low-light conditions.
- Action & Camera Control Buttons: Available across all models, enhancing user interaction and customization.
Summary of Contents
- iPhone 16: 6.1" Super Retina XDR OLED, A18 chip, Dynamic Island, and updated Safe Area Insets.
- iPhone 16 Plus: 6.7" display with identical specs to the iPhone 16 but improved battery life.
- iPhone 16 Pro: Upgraded to a 6.3" display, A18 Pro chip, ProMotion, and Always-On features.
- iPhone 16 Pro Max: Largest 6.9" display with all Pro features and improved dimensions.
- Complete Screen Size List: Apple now supports 13 different iPhone screen sizes, emphasizing the need for responsive designs.
Developer Takeaways
- Safe Area Insets: Adjust layouts to accommodate varying insets for status bars and screen edges.
- App Store Screenshots: Only one set of screenshots required, targeting the largest devices (6.9" or 6.5").
- Minimum Deployment Target: Ensure apps support iOS 13 and above to cover all iPhone models.
Additional Resources
Persistance
🔵 Different Ways of Storing Images in CoreData
This post explores different strategies for storing images in CoreData, focusing on performance, memory usage, and compatibility with iCloud sync. The author walks through five methods and provides detailed insights into their performance metrics.
Details
Published: 2024-09-18
Tags:
CoreData, Swift, UIImage, iCloud, Persistence
Key Points
- Explore various strategies for storing images in CoreData.
- Analyze performance, disk space usage, and RAM consumption for each approach.
- The focus is on finding the most efficient method compatible with iCloud sync.
Summary of Contents
-
Basic Setup:
Creating a separatePhotoentity with a one-to-many relationship withItemto help CoreData efficiently manage memory. -
Option 1: Binary Data + External Storage:
Storing image data with external storage enabled works but may present challenges when adding iCloud sync. -
Option 2: NSKeyedArchiver with Transformable Property:
This option, while functional, results in slow performance and high disk/RAM usage. -
Option 3: UIImage.jpegData with Transformable Property:
This method offers a balance between performance, disk usage, and compatibility. -
Option 4: UIImage.pngData with Transformable Property:
This method leads to larger files and slow performance, making it less practical. -
Option 5: Storing Original Data from Photos Library:
Storing the original image data directly is the most efficient, but it has limitations regarding direct camera use and permissions.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 Apple Documentation on CoreData: Learn about CoreData fundamentals.
- 🔗 Best Practices for iCloud Integration: A guide to adding iCloud support in your app.
Swift
🔵 Storing Two Types in the Same Variable Using Either
In this blog post, we explore a practical and elegant solution to handling heterogeneous data types in SwiftUI applications using the Either type. By leveraging the flexibility of Either, you can easily store different types in the same variable and refactor your SwiftUI views efficiently. The article walks through the process of displaying ads along with movies in a list, providing a clean and maintainable codebase.
Details
URL: 🔗 Storing Two Types in the Same Variable Using Either
Published: 2024-09-18
Authors: Vincent
Tags:
Swift, SwiftUI, Generics, Identifiable
Key Points
- Use
Eitherto store values of two different types in a single variable. - Improve code maintainability and readability by refactoring SwiftUI views.
Eitheris similar to Swift'sResult, but can store any type instead of restricting toError.- Refactor
Listviews usingEitherto handle heterogeneous data, such as displaying movies and ads together.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: Discusses the problem of managing heterogeneous data and introduces
Eitheras a solution. - Refactoring with Either: Demonstrates how to refactor code to handle different data types in a SwiftUI
Listusing theEitherenum. - Conditional Conformance to Identifiable: Explains how to ensure that both types in
Eitherconform toIdentifiablewhen necessary. - Final Refactor: Provides an example of refactored code that uses
Eitherto manage movies and ads in the same list.
Additional Resources
- Either Enum Documentation: Learn more about Swift's enum types and their capabilities.
- SwiftUI List Documentation: Understand how to work with dynamic lists in SwiftUI.
🔵 Static, V-Table, and Message Dispatches in Swift
This article explores how method dispatches work in Swift, breaking down their types, behaviors, and the optimizations made by the compiler and runtime to efficiently resolve method calls.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://betterprogramming.pub/a-deep-dive-into-method-dispatches-in-swift-65a8e408a7d0
Authors: Neel Bakshi
Tags:
swift, method-dispatch, ios-development, runtime-optimization, dynamic-dispatch
Key Points
- Definition: Method dispatches manage how functions are called and resolved during compile-time or runtime.
- Types of Dispatches:
- Static Dispatch: Used for methods that cannot be overridden. Fastest type due to direct memory address lookup.
- V-Table Dispatch: Default for class methods. Uses compile-time tables to resolve method calls at runtime, supporting inheritance.
- Message Dispatch: Enables Objective-C dynamic runtime capabilities like method swizzling and KVO.
- Optimizations: Includes mechanisms like the
finaland@objckeywords to control dispatch behavior.
Summary of Contents
- Introduction: Explains the role of dispatch mechanisms in resolving method calls.
- Static Dispatch: Demonstrates its usage with
staticandfinalkeywords. - V-Table Dispatch: Explains the use of V-Tables for resolving overridden and non-overridden class methods, referencing SIL (Swift Intermediate Language) generation.
- Message Dispatch: Covers its runtime flexibility and interaction with Objective-C runtime via
@objcanddynamic. - SIL Insights: Includes examples of SIL-generated code to highlight differences in dispatch mechanisms.
- Trade-Offs: Discusses performance impacts and use cases of each dispatch type.
Helpful Links
- 🔗 Method Dispatches in Swift — RightPoint
- 🔗 @objc and dynamic SIL walkthrough — Swift Unboxed
- 🔗 Reducing dynamic dispatches — Apple Swift Blog
🔵 Understanding Swift Closures
This blog post explores the intricacies of closures in Swift, highlighting advanced topics like reference cycles, capture lists, and their use as reference types. It supplements Swift's official documentation by delving into nuanced scenarios and practical considerations for developers.
Details
URL: 🔗 Understanding Swift Closures
Published: 2023-05-27
Authors: Vitaly Batrakov
Tags:
[Swift], [Closures], [Memory Management], [Reference Cycles], [Capture Lists]
Key Points
-
Definition and Forms
Closures are blocks of functionality, akin to functions, that can be passed around and executed. They come in three forms: global functions, nested functions, and closure expressions. -
Reference Types
Closures are stored in the heap and considered reference types, meaning they can create strong references, impacting memory management. -
Capture Lists
Capture lists allow control over how variables are captured in closures, using modifiers likeweakandunownedto avoid retain cycles. -
Escaping vs. Non-Escaping Closures
@escapingclosures persist beyond their defining scope, potentially creating reference cycles, while non-escaping closures are automatically deallocated.
Summary of Contents
-
Introduction to Closures
Covers the basic definition, forms of closures, and their role as first-class objects in Swift. -
Memory Management and Retain Cycles
Explains how closures can create reference cycles and provides solutions like capture lists withweakorunownedreferences. -
Capture List Nuances
Demonstrates how value and reference types behave differently in capture lists, using examples for clarity. -
Nested Functions as Closures
Highlights that nested functions behave like closures and can capture values from their surrounding context. -
Advanced Scenarios
Discusses unobvious retain cases and how assigning methods to closures implicitly capturesself. -
Understanding Closure Type
Concludes that closures, as reference types, can persist captured value types by moving them to the heap.
Additional Resources
- Swift Documentation: 🔗 The Swift Programming Language: Closures
- Related Blog: 🔗 Multiple Trailing Closures in Swift
🔵 Escaping vs Non-Escaping Closures in Swift
Swift simplifies many aspects of development, but some features require deeper understanding, such as escaping and non-escaping closures. This article explains the difference between these closure types, the evolution of @escaping, and the deprecation of @noescape in Swift 3.
Details
URL: 🔗 What Do Escaping and Noescape Mean in Swift 3?
Published: 2024-11-21
Authors: Bart Jacobs
Tags:
Swift, Closures, @escaping, @noescape, Memory Management
Key Points
- Escaping Closures: Invoked after the function returns and require explicit
@escapingin Swift 3. - Non-Escaping Closures: Now the default, simplifying code and improving performance.
- @escaping Attribute: Lets the compiler know the closure might outlive the function's execution.
- Deprecation of @noescape: Simplifies closure handling in Swift 3 by making closures non-escaping by default.
Summary of Contents
- What Is @noescape? Explanation of the deprecated attribute and its use in Swift 2.
- What Are Escaping Closures? Description of closures that outlive their function scope and when they occur.
- The Transition to Swift 3: Introduction of
@escaping, making non-escaping closures the default. - Why It Matters: Benefits like performance optimizations and safer memory management.
Additional Resources
- Swift Evolution Proposal: 🔗 SE-0103: Make Non-Escaping Closures the Default
- Apple Documentation: 🔗 Closures
- Twitter Discussion: 🔗 Bart Jacobs
Networking
🔴 "Network Connectivity on iOS with Swift"
Learn best practices for handling network connectivity in iOS applications using Swift. This article dives into reliable methods, addressing common scenarios like checking connectivity, enabling/disabling app features, and attaching constraints to network operations. It highlights why outdated methods like SCNetworkReachability should be avoided and introduces modern solutions recommended by Apple, including Adaptable Connectivity APIs and NWPathMonitor.
Details
URL: 🔗 Network Connectivity on iOS with Swift
Published: [Insert Date Here]
Authors: Vadim Bulavin
Tags:
networking, swift, ios-development, urlsession, nwpathmonitor
Key Points
- Avoid pre-flight checks: Avoid relying on
SCNetworkReachabilityfor determining internet availability. - Use Adaptable Connectivity APIs: Enable the
waitsForConnectivityflag inURLSessionConfigurationfor seamless request handling. - Leverage NWPathMonitor: Monitor network status changes in real-time.
- Adopt Low Data Mode: Respect user preferences for constrained networks with
allowsConstrainedNetworkAccess.
Summary of Contents
- Why Avoid Pre-flight Checks: Explanation of inherent race conditions and unreliability.
- Enabling Adaptable Connectivity: Demonstrates using
URLSessionConfigurationwith code examples. - Handling Connectivity UI Updates: Use
URLSessionDelegateorNWPathMonitorfor real-time UI adjustments. - Network Operation Constraints: Best practices for managing data usage, like adopting Low Data Mode or disabling expensive network operations.
Additional Resources
- Apple Documentation: 🔗 Networking Overview
- WWDC Videos: 🔗 Advances in Networking, Part 1, 🔗 Part 2
Swift on Server
🟢 Dev Containers for Swift: How to Debug and Run Applications in VS Code
Learn how Dev Containers in VS Code streamline Swift development for server apps by enabling a consistent Docker-based development and debugging environment. This article dives deep into setting up, configuring, and leveraging Dev Containers to debug, run, and test Swift applications, ensuring uniform results across development and deployment environments.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://swifttoolkit.dev/posts/dev-containers-swift
Published: 2024-11-04
Authors: SwiftToolkit.dev
Tags:
Swift, Dev Containers, VS Code, Docker, Swift Server, Debugging
Key Points
- Dev Containers simplify Swift development by running applications inside Docker containers for consistency across environments.
- VS Code Extensions: Leverage the Swift and Dev Containers extensions to debug and run apps.
- Ease of Use: No need to manually configure Dockerfiles for simple projects.
- Port Forwarding: Forward container ports seamlessly to the host for access to running services.
Summary of Contents
- Running the Sample App: Demonstrates using a Hummingbird-based Todo app with Postgres integration.
- VS Code Configuration: Steps for setting up the Swift extension and launch configurations in
launch.json. - Debugging on macOS: Using the Argument Parser and Swift Package Manager for a seamless debugging experience.
- Using Dev Containers: Setting up and running Swift apps inside containers with a minimal
devcontainer.jsonconfiguration. - Debugging with Breakpoints: Walkthrough of adding and leveraging breakpoints in Dev Containers.
Additional Resources
- Swift Server Work Group: 🔗 Swift Extension for VS Code
- Hummingbird Samples: 🔗 Sample Projects Repository
- Docker Alternatives: 🔗 Orbstack for lightweight macOS containerization.
Testing
🔵 How to Test UIKit & SwiftUI Views? Explained with Memes
Testing UI components in iOS development can be challenging, especially with the transition from UIKit to SwiftUI. This post explores strategies for testing both UIKit and SwiftUI views, with a focus on snapshot testing and its practical applications, limitations, and best practices.
Details
URL: 🔗 https://swiftandmemes.com/how-to-test-uikit-swiftui-views-explained-with-memes/
Published: 2023-06-01
Authors: Pawel Kozielecki
Tags:
[Snapshot Testing], [SwiftUI], [UIKit], [UI Testing]
Key Points
- Snapshot Testing: A powerful integration testing approach that verifies the UI against pre-recorded snapshots of expected outputs.
- Testing Strategies: Strategies differ between UIKit and SwiftUI, with UIKit allowing more direct property traversal.
- Limitations: Challenges include testing animations, managing device-specific differences, and maintaining snapshots across iOS updates.
- Best Practices: Use snapshot tests for reusable components like error screens or custom controls to detect regressions during refactoring.
Summary of Contents
- Snapshot Testing Basics: An overview of what snapshot testing is and how it works.
- Implementing Snapshot Tests for SwiftUI: Demonstrating the process using a
UIHostingViewControllerand view models. - Testing UIKit Views: A guide to setting up snapshot tests for
UIViewandUIViewControllercomponents. - Challenges and Limitations: Addressing issues like animations, CI pipeline setups, and iOS version changes.
- Practical Tips: Recommendations on prioritizing views to test and integrating snapshot testing into development workflows.
Additional Resources
- 🔗 Swift Snapshot Testing Library: A library for implementing snapshot tests.
- 🔗 KISS Your SwiftUI Views: A post exploring best practices for SwiftUI view design.
- 🔗 SwiftUI Router Tests: Examples of testing SwiftUI navigation and views.